A Journey Across the Largest Continent: Exploring the Map of Asia and its Countries
Related Articles: A Journey Across the Largest Continent: Exploring the Map of Asia and its Countries
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Across the Largest Continent: Exploring the Map of Asia and its Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Across the Largest Continent: Exploring the Map of Asia and its Countries

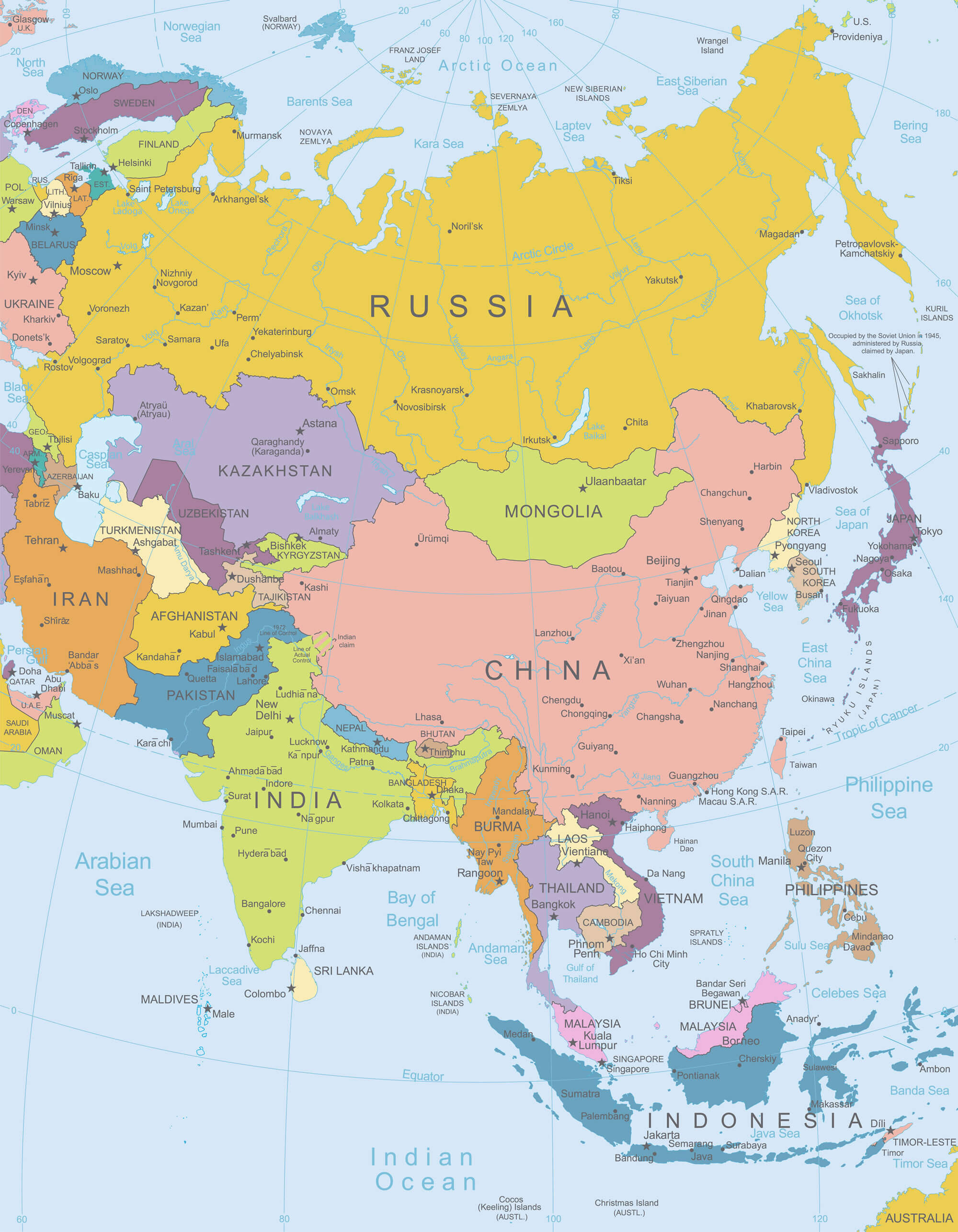
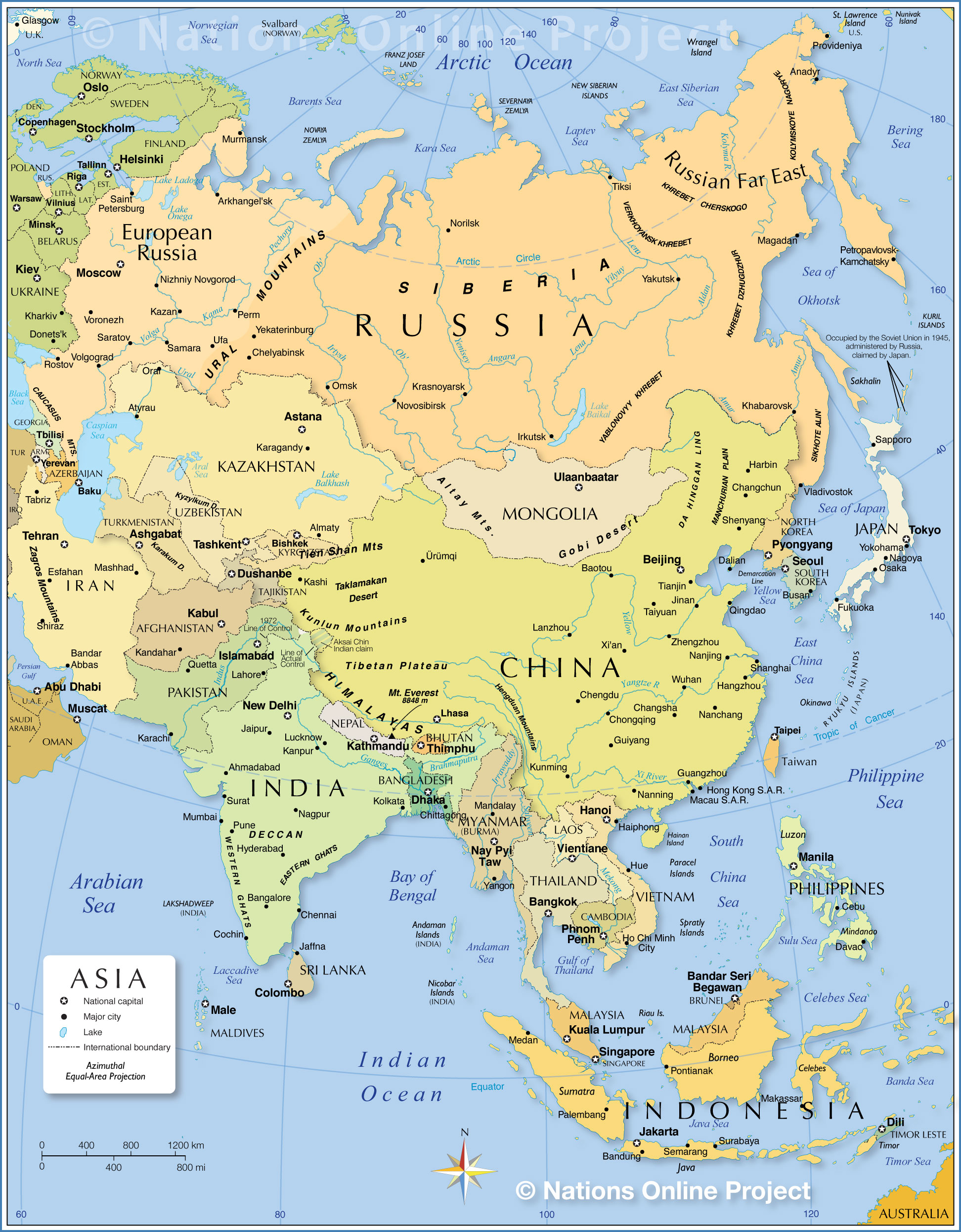
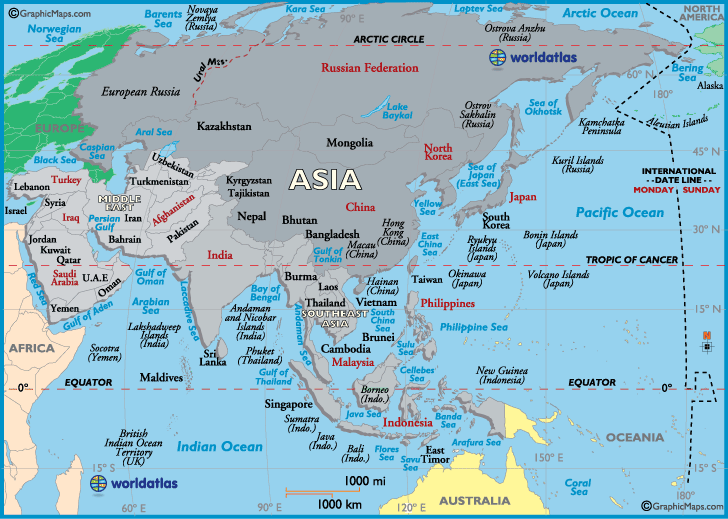
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich cultures, and vibrant histories. Its sprawling expanse, encompassing 44.6 million square kilometers, is home to 49 distinct countries, each with its unique identity, challenges, and contributions to the global stage. Understanding the map of Asia and its constituent nations is crucial to appreciating the continent’s complexities and its impact on the world.
A Geographical Overview: From the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea
Asia’s vastness is immediately apparent when examining a map. Stretching from the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the Pacific Ocean, and from the Arctic Circle to the Indian Ocean, the continent encompasses a breathtaking range of geographical features.
- Mountains: The majestic Himalayas, home to Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak, define the northern boundary of South Asia. Other prominent mountain ranges include the Hindu Kush, the Pamir Mountains, and the Tian Shan, shaping the landscapes of Central Asia.
- Plateaus: The Tibetan Plateau, the world’s highest plateau, and the Deccan Plateau in India are significant geographical features, influencing climate and human settlements.
- Deserts: The vast Arabian Desert, the Gobi Desert, and the Taklamakan Desert are stark reminders of Asia’s arid landscapes.
- Rivers: The mighty Yangtze, Mekong, and Indus rivers, among others, are lifelines for millions, providing water for agriculture, transportation, and sustenance.
- Islands: Countless islands dot the Asian coastline, including the Indonesian archipelago, the Philippines, and the Japanese islands, each offering unique ecosystems and cultural identities.
A Mosaic of Cultures and Histories:
Asia’s geographical diversity is mirrored in its cultural and historical tapestry. The continent is a melting pot of ethnicities, religions, and languages, each contributing to the rich mosaic that defines Asian identity.
- Ancient Civilizations: From the Indus Valley Civilization to the Mesopotamian civilizations, Asia has been a cradle of human civilization for millennia. Ancient empires, including the Chinese dynasties, the Mughal Empire, and the Roman Empire, left lasting legacies on the continent’s cultural landscape.
- Religious Diversity: Asia is home to some of the world’s major religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, and Confucianism. These faiths have profoundly shaped societal values, traditions, and artistic expressions across the continent.
- Linguistic Variety: Asia is a linguistic wonderland, with over 2,300 languages spoken across its diverse regions. From the Indo-European languages of South Asia to the Altaic languages of Central Asia and the Sino-Tibetan languages of East Asia, the continent’s linguistic diversity reflects its complex history and cultural interactions.
Exploring the Countries: A Glimpse into Asia’s Diversity
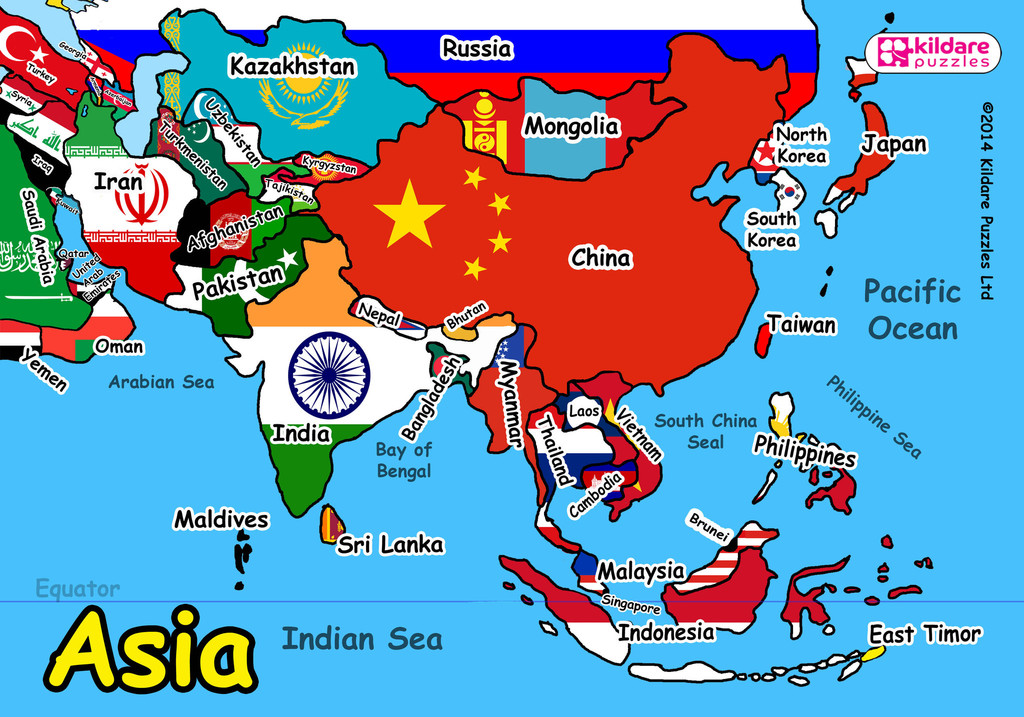
Examining the map of Asia reveals a fascinating array of countries, each with its unique character and contributions to the world. Here are a few examples:
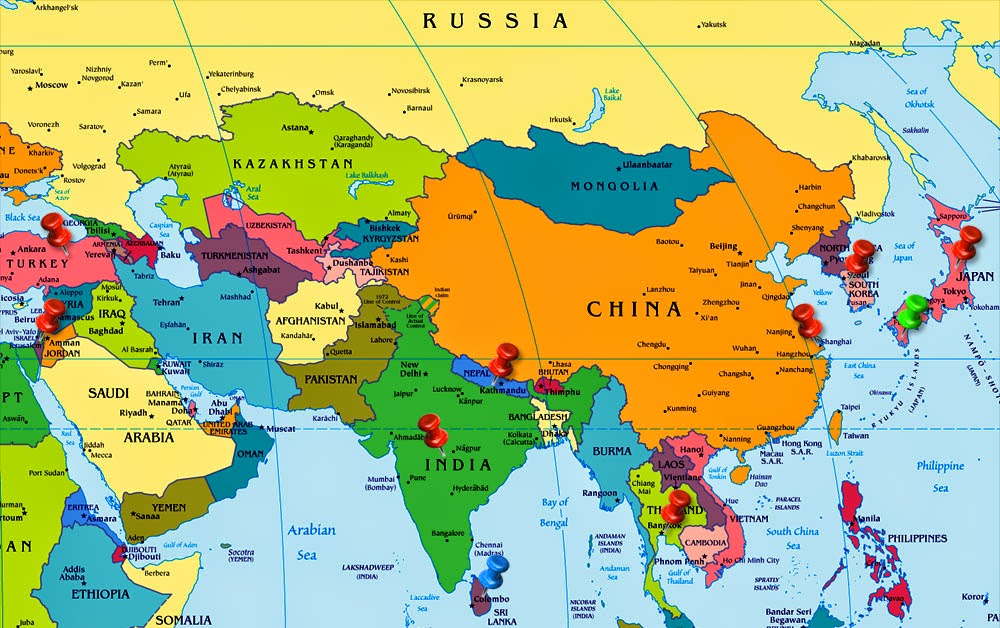
- China: The world’s most populous country, China is a powerhouse in terms of economic growth, technological advancement, and cultural influence. Its vast territory, spanning from the Himalayas to the South China Sea, is home to diverse ethnicities and landscapes.
- India: The second most populous country in the world, India is a vibrant democracy with a rich history and a thriving economy. Its cultural diversity, encompassing Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Christianity, and other faiths, makes it a unique and fascinating destination.
- Japan: A technologically advanced nation known for its high-quality products, Japan is also a cultural powerhouse, renowned for its traditional arts, cuisine, and animation. Its unique island location has fostered a distinct sense of national identity.
- Indonesia: The world’s largest archipelago, Indonesia is home to over 17,000 islands and a diverse population. Its rich cultural heritage, influenced by Hinduism, Buddhism, and Islam, is reflected in its vibrant arts, music, and cuisine.
- Russia: Spanning vast swathes of land across Europe and Asia, Russia is a geopolitical powerhouse with a rich history and a unique cultural identity. Its vast territory and diverse landscapes offer a glimpse into the continent’s vastness.
The Importance of Understanding the Map of Asia
Understanding the map of Asia is essential for several reasons:
- Global Interconnectivity: Asia’s geographical location, bordering Europe and Africa, makes it a crucial link in the global network. Understanding its diverse cultures, languages, and political landscapes is essential for fostering international cooperation and understanding.
- Economic Powerhouse: Asia is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, including China, India, and South Korea. Its economic dynamism is shaping the global economic landscape and influencing international trade and investment.
- Cultural Exchange: Asia’s diverse cultures and traditions have enriched the world through its art, music, literature, and cuisine. Understanding the continent’s cultural tapestry fosters appreciation for the beauty and richness of human diversity.
- Environmental Challenges: Asia faces significant environmental challenges, including climate change, deforestation, and pollution. Understanding the region’s geography and its vulnerability to these issues is crucial for developing effective solutions and promoting sustainable development.
FAQs about the Map of Asia and its Countries
1. What are the major geographic features of Asia?
Asia is characterized by vast mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, the Hindu Kush, and the Tian Shan, as well as extensive plateaus like the Tibetan Plateau and the Deccan Plateau. Large deserts, such as the Arabian Desert and the Gobi Desert, also define the continent’s landscape. Additionally, numerous rivers, including the Yangtze, Mekong, and Indus, are vital lifelines for millions.
2. What are the major religions practiced in Asia?
Asia is home to a diverse range of religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, and Confucianism. These faiths have profoundly shaped societal values, traditions, and artistic expressions across the continent.
3. What are some of the most important countries in Asia?
Asia is home to numerous important countries, each with its unique contributions to the global stage. Some of the most significant include China, India, Japan, Indonesia, Russia, South Korea, and Singapore.
4. What are some of the major challenges facing Asia?
Asia faces several challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are significant concerns, while geopolitical tensions and conflicts also impact the region.
5. What are some of the opportunities for Asia in the future?
Asia has the potential for continued economic growth, technological advancement, and social progress. The region’s young population, growing middle class, and increasing investment in education and innovation offer opportunities for sustainable development and prosperity.
Tips for Studying the Map of Asia
- Visualize the Continent: Use a physical map to visualize the continent’s vastness and the relationships between its countries.
- Focus on Key Regions: Divide Asia into distinct regions, such as East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, Central Asia, and West Asia, to better understand their unique characteristics.
- Explore Cultural Differences: Research the history, languages, religions, and traditions of different countries to gain a deeper understanding of their cultural diversity.
- Connect Geography and History: Link geographical features to historical events and cultural developments to understand how they have shaped the continent’s landscape.
- Engage with Current Events: Stay informed about current events in Asia to gain insights into the challenges and opportunities facing the region.
Conclusion
The map of Asia and its countries is a window into a world of astonishing diversity, ancient cultures, and global significance. From the towering Himalayas to the bustling metropolises, from the serene temples to the vibrant marketplaces, Asia is a continent that continues to captivate and inspire. Understanding its geography, history, and cultures is crucial for appreciating its complexities and its role in shaping the future of our world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Across the Largest Continent: Exploring the Map of Asia and its Countries. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!