A Journey Across Asia: A Geographic Overview of the Continent
Related Articles: A Journey Across Asia: A Geographic Overview of the Continent
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Across Asia: A Geographic Overview of the Continent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Across Asia: A Geographic Overview of the Continent

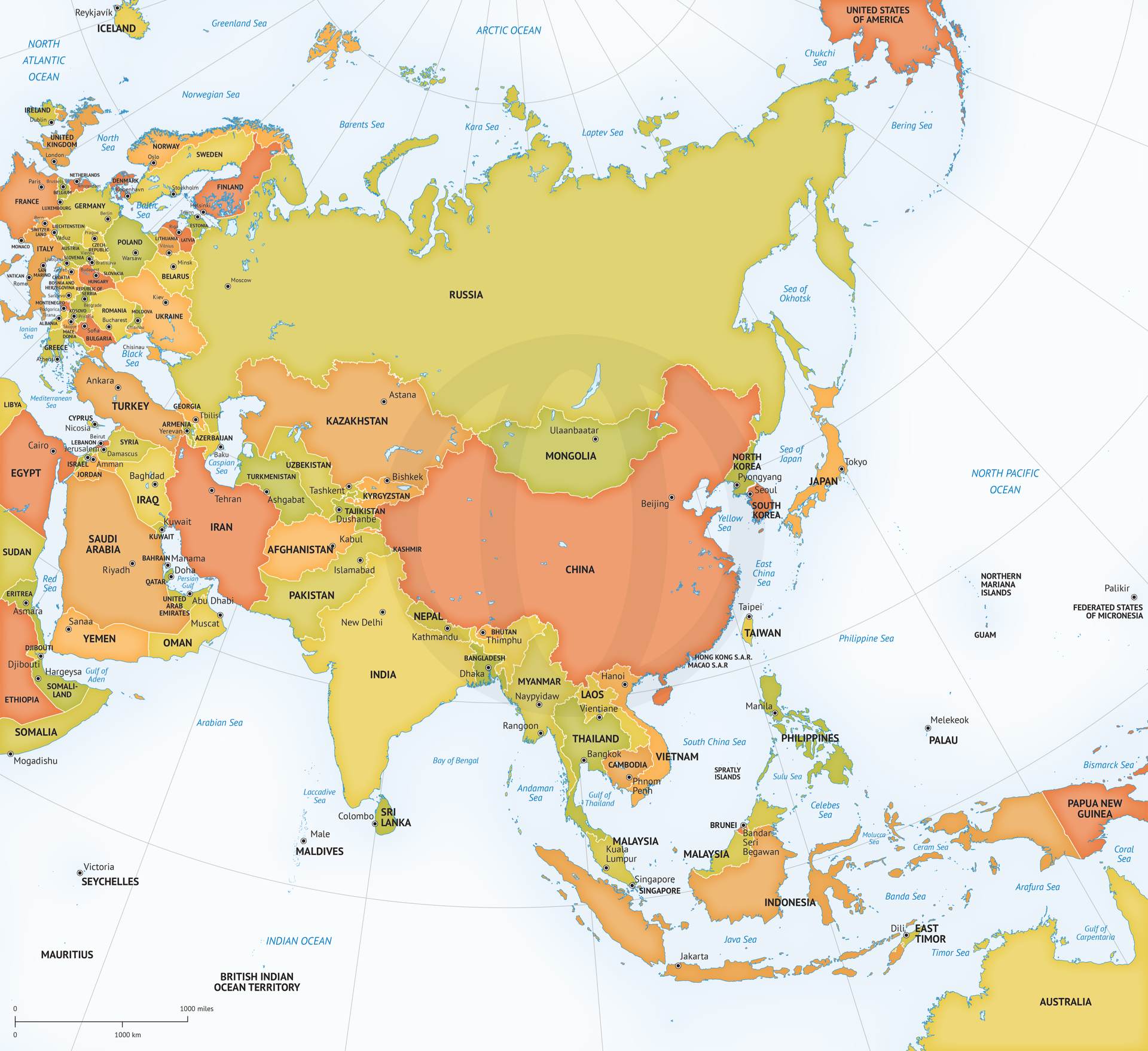
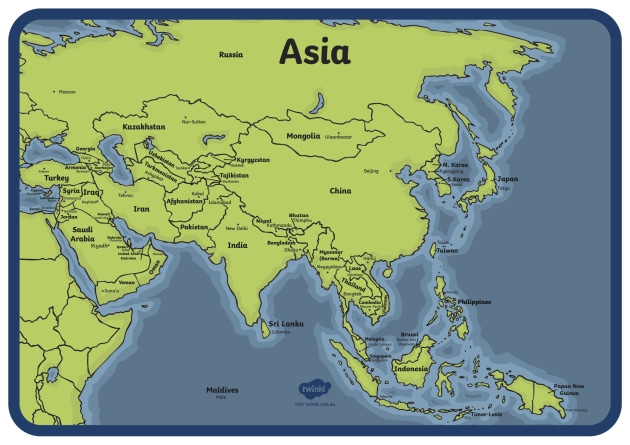
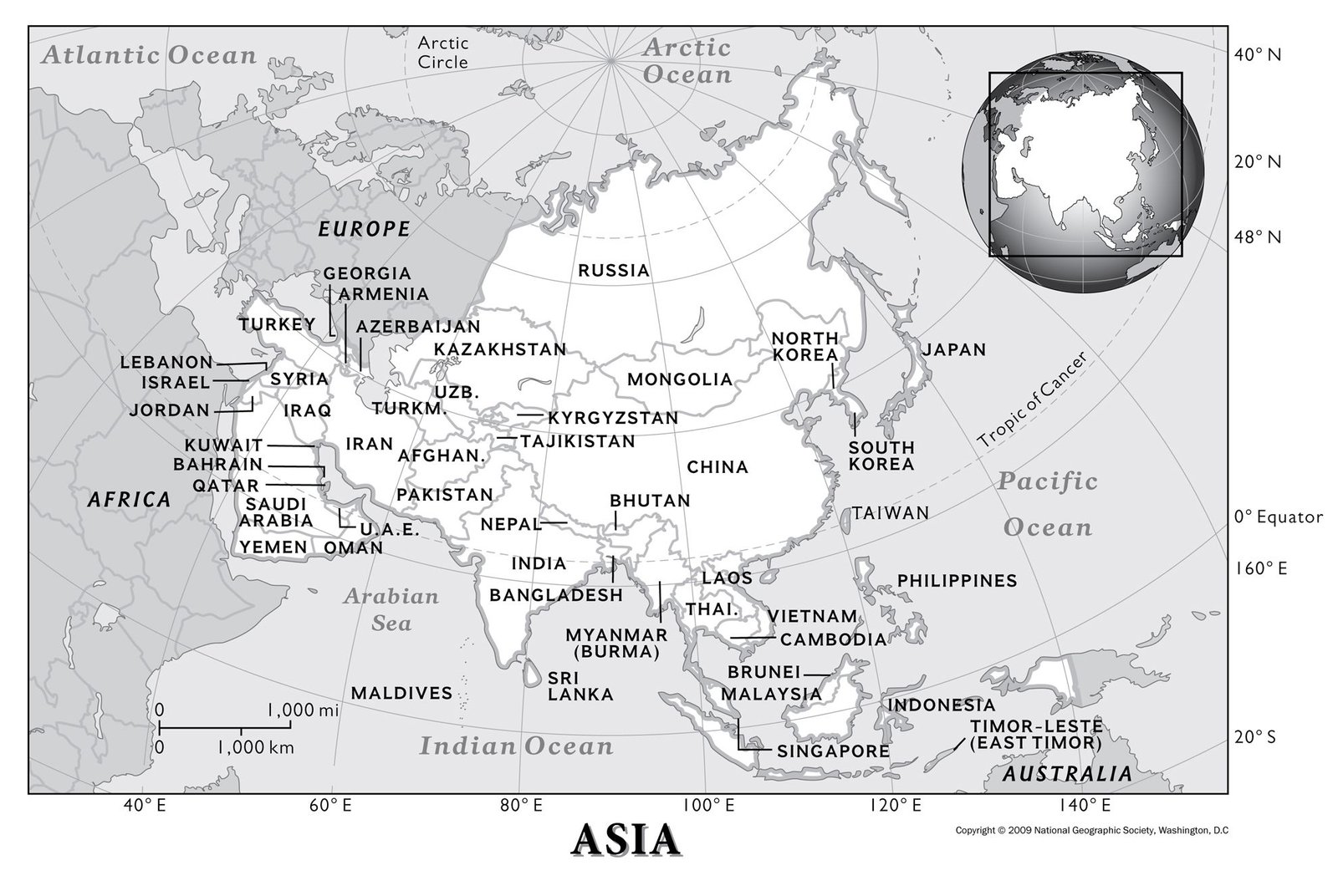
Asia, the largest and most populous continent on Earth, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories. Its sprawling expanse, stretching from the frigid Arctic to the tropical islands of the Indian Ocean, encompasses 49 countries, each with its own unique story to tell. Understanding the geographic layout of Asia, with its intricate network of countries, is crucial for grasping the continent’s complex dynamics and its profound impact on the world stage.
A Continental Jigsaw: Understanding the Asian Landscape
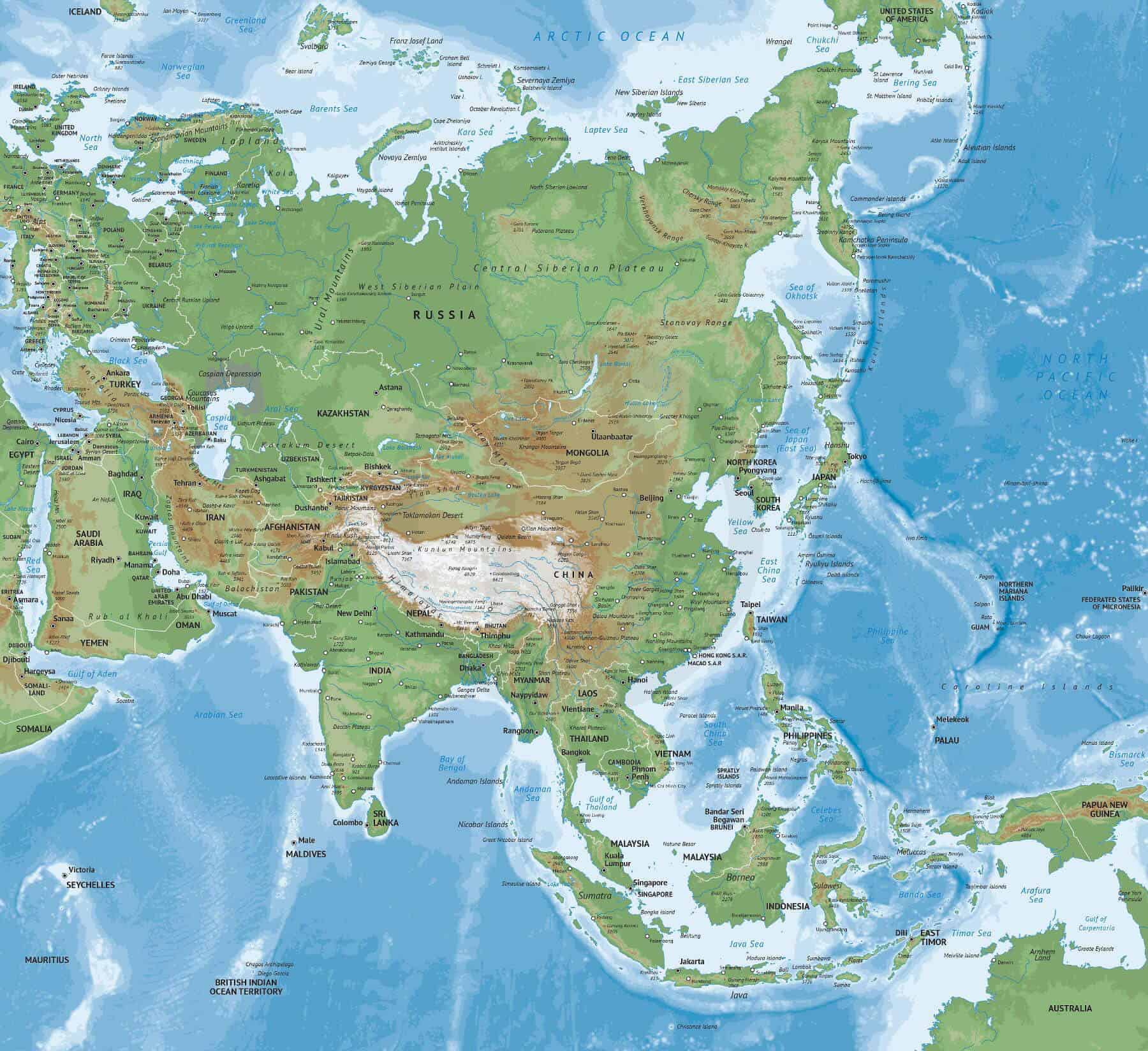
The map of Asia is a visual testament to the continent’s immense scale and geographical diversity. From the towering Himalayas in the north to the fertile plains of the Ganges Delta in the south, Asia’s landscape is a kaleidoscope of contrasts.
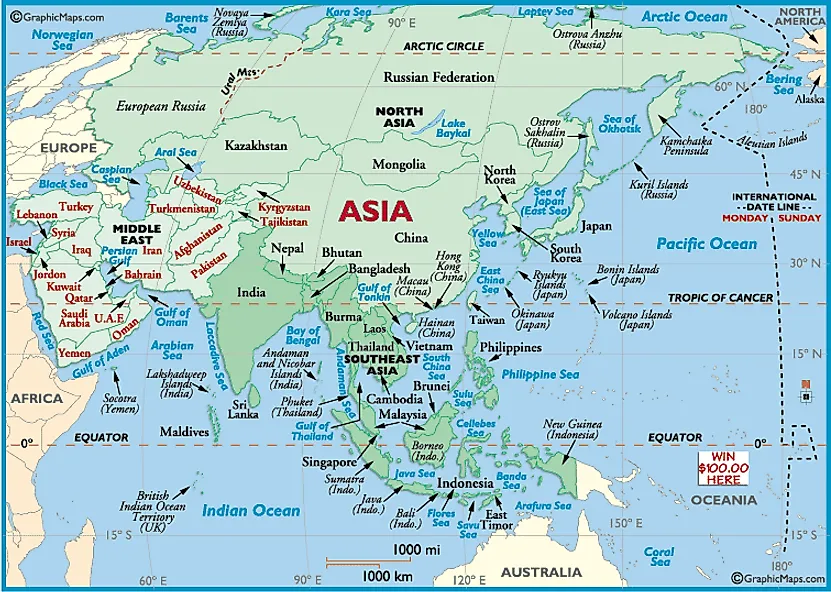
Eastern Asia: This region, characterized by its mountainous terrain and vast coastal plains, is home to some of the world’s most populous and influential nations. China, the largest country in the region, shares a border with Russia to the north and is flanked by the Korean Peninsula to the east. Japan, a nation of islands, lies off the coast of mainland Asia, while the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea) occupy the Korean Peninsula. Mongolia, a landlocked country in the north, completes the picture of Eastern Asia.
Southeast Asia: This region is a melting pot of cultures and languages, with a diverse topography that includes dense rainforests, fertile river deltas, and volcanic islands. Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, and Malaysia lie on the mainland, while the island nations of Singapore, Indonesia, Brunei, the Philippines, and East Timor complete the Southeast Asian mosaic.
South Asia: Home to the Indian subcontinent, this region is defined by its vast plains, towering mountain ranges, and diverse coastal regions. India, the second most populous country in the world, dominates the region, sharing borders with Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and China. Pakistan, located to the west of India, is a country with a rich history and a complex geopolitical landscape. Sri Lanka, an island nation off the coast of India, is known for its stunning beaches and ancient ruins. The landlocked nations of Nepal and Bhutan, nestled in the Himalayas, are renowned for their natural beauty and cultural heritage. Bangladesh, located in the fertile delta of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, is a densely populated country with a vibrant culture.
Central Asia: This region, situated between Eastern Europe and South Asia, is characterized by its arid plains, vast deserts, and towering mountains. The five countries of Central Asia – Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan – are strategically located along the historic Silk Road, making them vital crossroads for trade and cultural exchange.
Western Asia: This region, often referred to as the Middle East, is a complex and dynamic area with a rich history and diverse cultural landscape. Turkey, with its strategic location bridging Europe and Asia, is a key player in the region. The Arabian Peninsula, home to the oil-rich nations of Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Yemen, and Qatar, is a vital center for global energy production. Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, located in the eastern Mediterranean region, have played a significant role in shaping the history of the Middle East.
Northern Asia: This region, encompassing Russia’s vast Siberian territory, is characterized by its harsh climate, vast forests, and abundant natural resources. Russia’s presence in Northern Asia extends to the Arctic Ocean, where it shares borders with Norway, Finland, and the Baltic states.
The Importance of Understanding Asia’s Geography
A thorough understanding of Asia’s geography is crucial for comprehending the continent’s diverse cultures, economies, and geopolitical dynamics. The geographical features of Asia have shaped its history, its cultural identities, and its global influence.
- Economic Powerhouse: Asia’s vast resources, including oil, natural gas, minerals, and agricultural land, have fueled its economic growth. The region is home to some of the world’s largest economies, including China, Japan, India, and South Korea.
- Cultural Crossroads: Asia’s diverse landscapes and histories have resulted in a rich tapestry of cultures and traditions. From the ancient temples of Angkor Wat in Cambodia to the bustling markets of Istanbul, Turkey, Asia offers a glimpse into a fascinating array of cultural experiences.
- Geopolitical Importance: Asia’s strategic location, connecting continents and oceans, has made it a focal point for global politics. The region’s complex geopolitical landscape has shaped international relations and played a vital role in shaping global events.
FAQs: Navigating the Asian Landscape
Q: What is the largest country in Asia?
A: China, with a land area of 9,596,960 square kilometers, is the largest country in Asia.
Q: What is the most populous country in Asia?
A: China, with a population of over 1.4 billion people, is the most populous country in Asia.
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Asia?
A: The major mountain ranges in Asia include the Himalayas, the Hindu Kush, the Karakoram, the Tian Shan, and the Altai Mountains.
Q: What are the major rivers in Asia?
A: The major rivers in Asia include the Yangtze River, the Yellow River, the Ganges River, the Indus River, the Mekong River, and the Irrawaddy River.
Q: What are the major deserts in Asia?
A: The major deserts in Asia include the Gobi Desert, the Taklamakan Desert, the Thar Desert, and the Arabian Desert.
Tips for Understanding Asia’s Geography
- Use a map: A physical map of Asia is an invaluable tool for understanding the continent’s geography.
- Study the major geographical features: Familiarize yourself with the major mountain ranges, rivers, deserts, and coastal areas of Asia.
- Explore the countries: Learn about the individual countries of Asia, their histories, cultures, and economies.
- Read about the region’s history: A deep understanding of Asia’s history is crucial for comprehending its current geopolitical dynamics.
Conclusion: A Continent of Endless Discovery
The map of Asia is a testament to the continent’s immense scale and its diverse array of landscapes, cultures, and histories. From the towering Himalayas to the bustling cities of Tokyo and Mumbai, Asia is a continent of endless discovery, offering a glimpse into a fascinating world of human experience. Understanding Asia’s geography is not merely an academic pursuit; it is a key to unlocking the continent’s potential and appreciating its profound impact on the global stage.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Across Asia: A Geographic Overview of the Continent. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!