A Geographical Overview of Asia and the Middle East: Understanding the Region’s Complexities
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview of Asia and the Middle East: Understanding the Region’s Complexities
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview of Asia and the Middle East: Understanding the Region’s Complexities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview of Asia and the Middle East: Understanding the Region’s Complexities
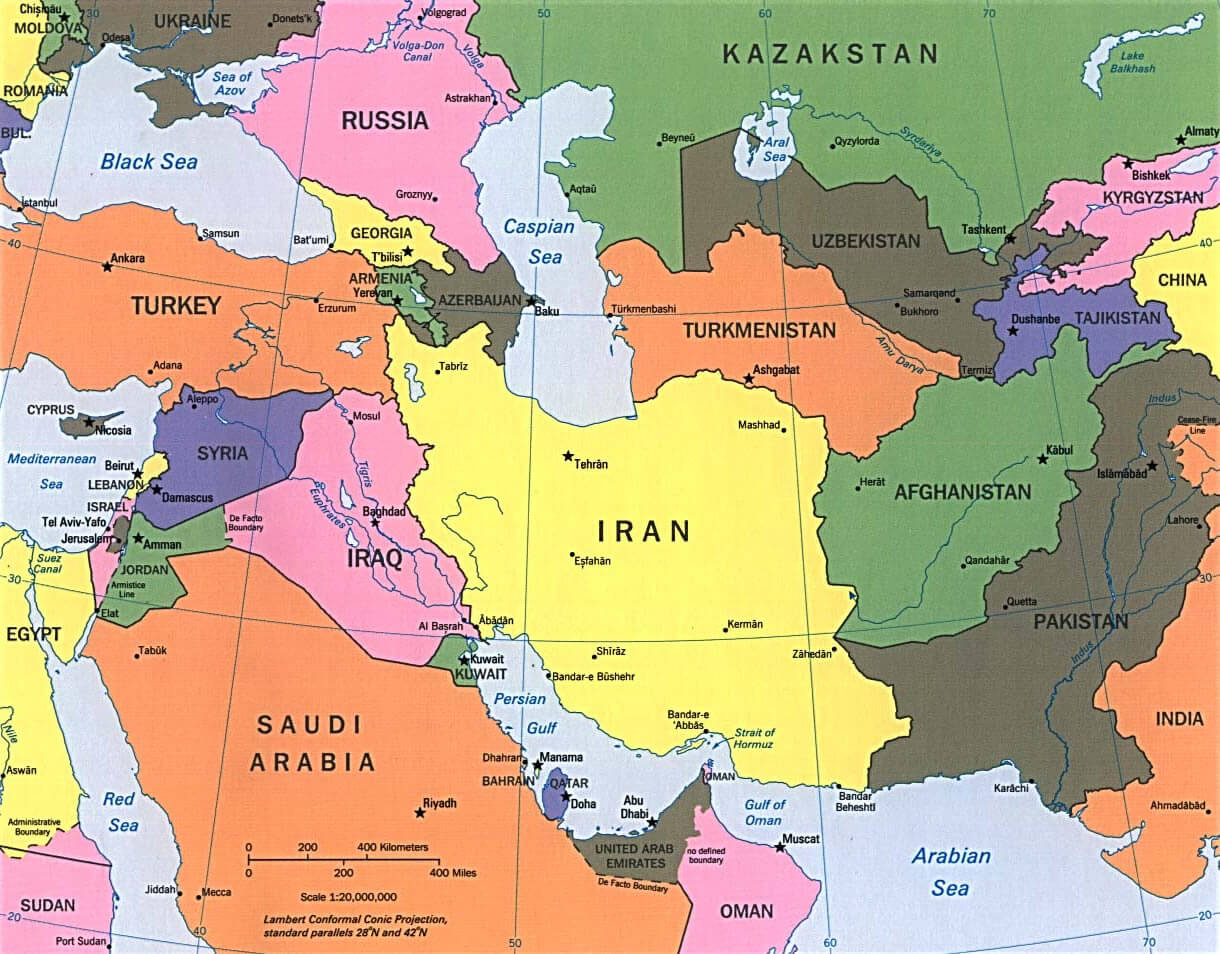
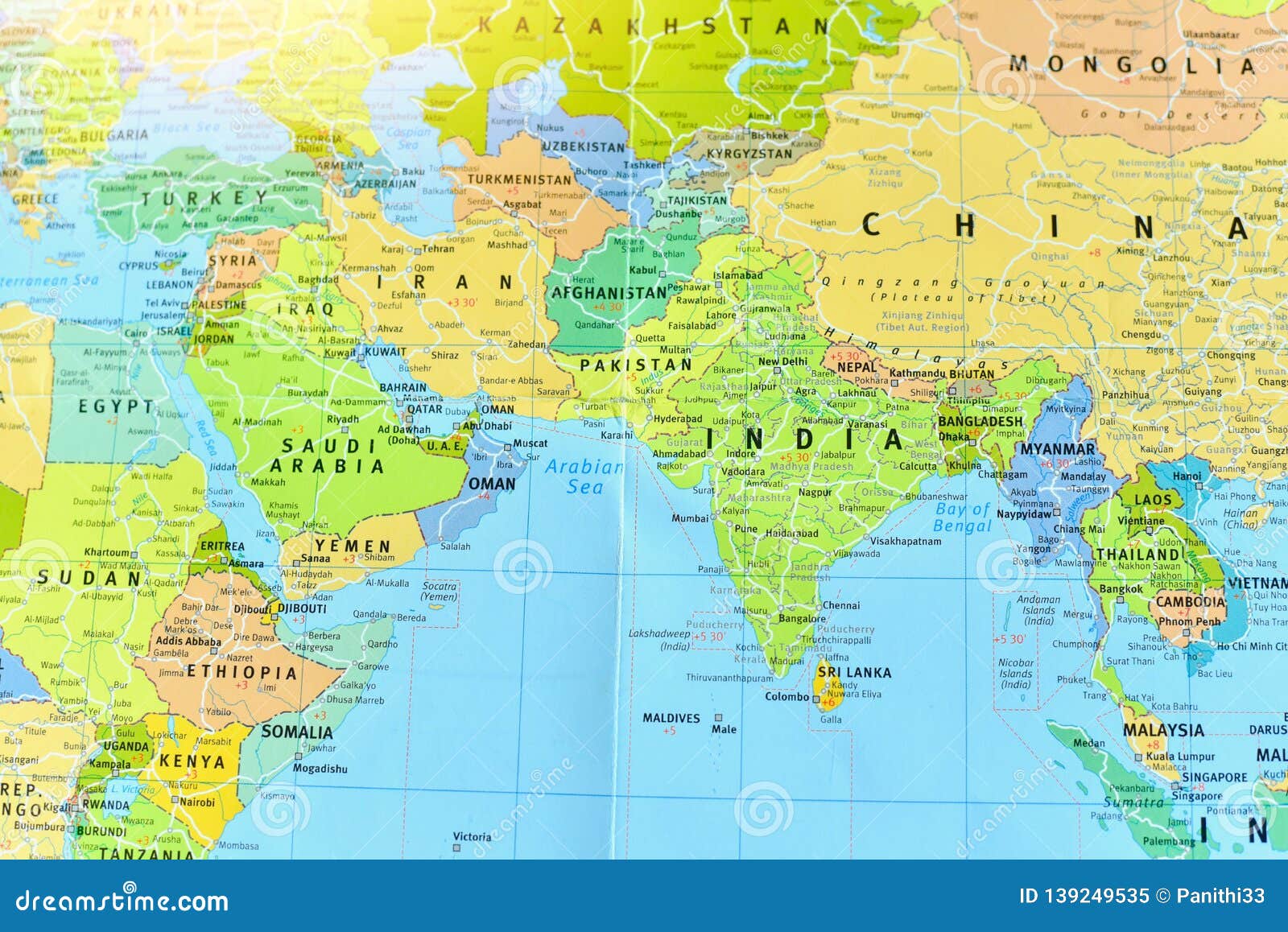
The vast expanse of Asia and the Middle East encompasses a diverse tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and geopolitical realities. This region, spanning from the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the Pacific Ocean, holds immense historical, cultural, and economic significance. Understanding the geography of this area is crucial for navigating its complexities and appreciating the interconnectedness of its nations.
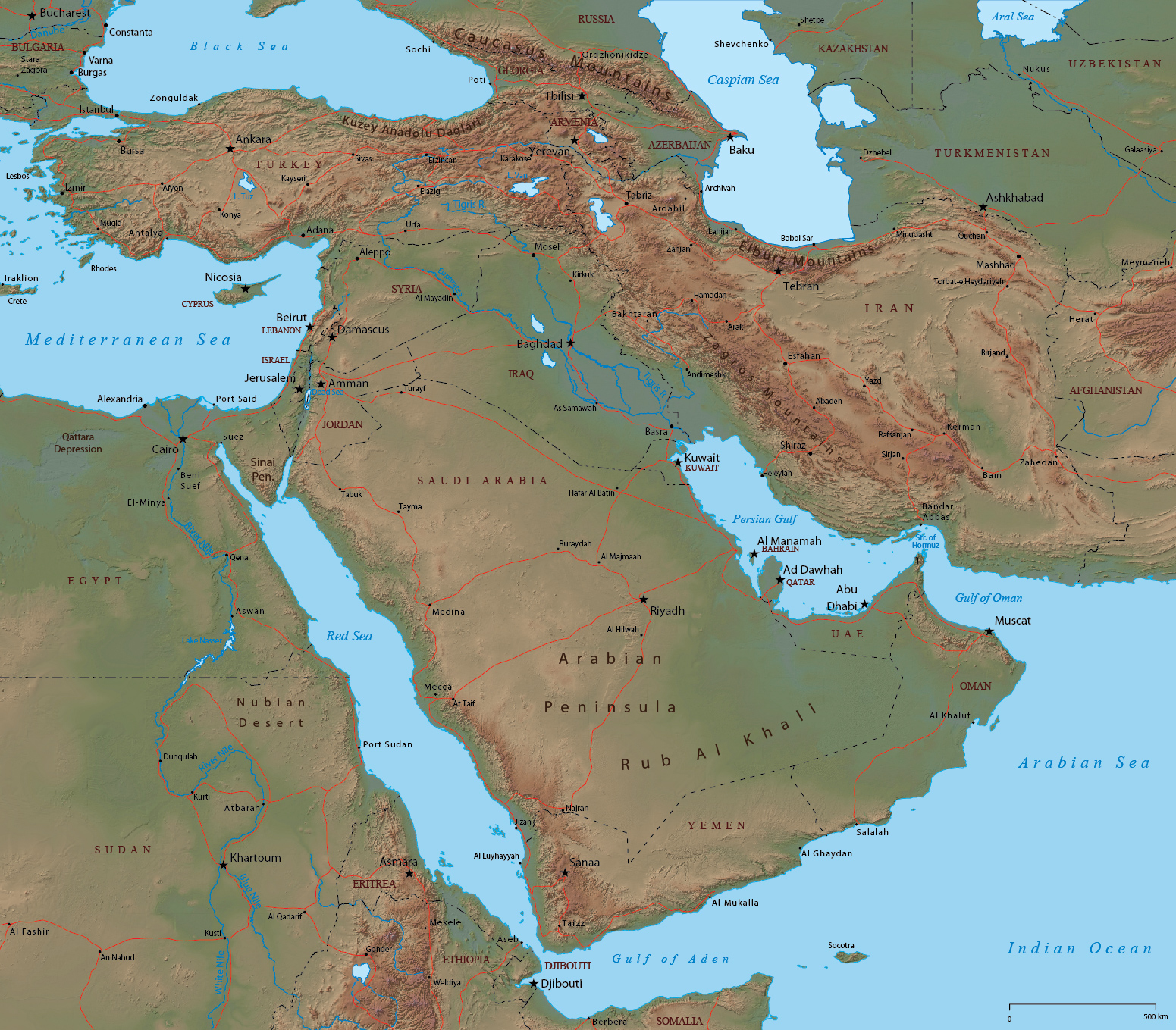
A Look at the Map: A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes
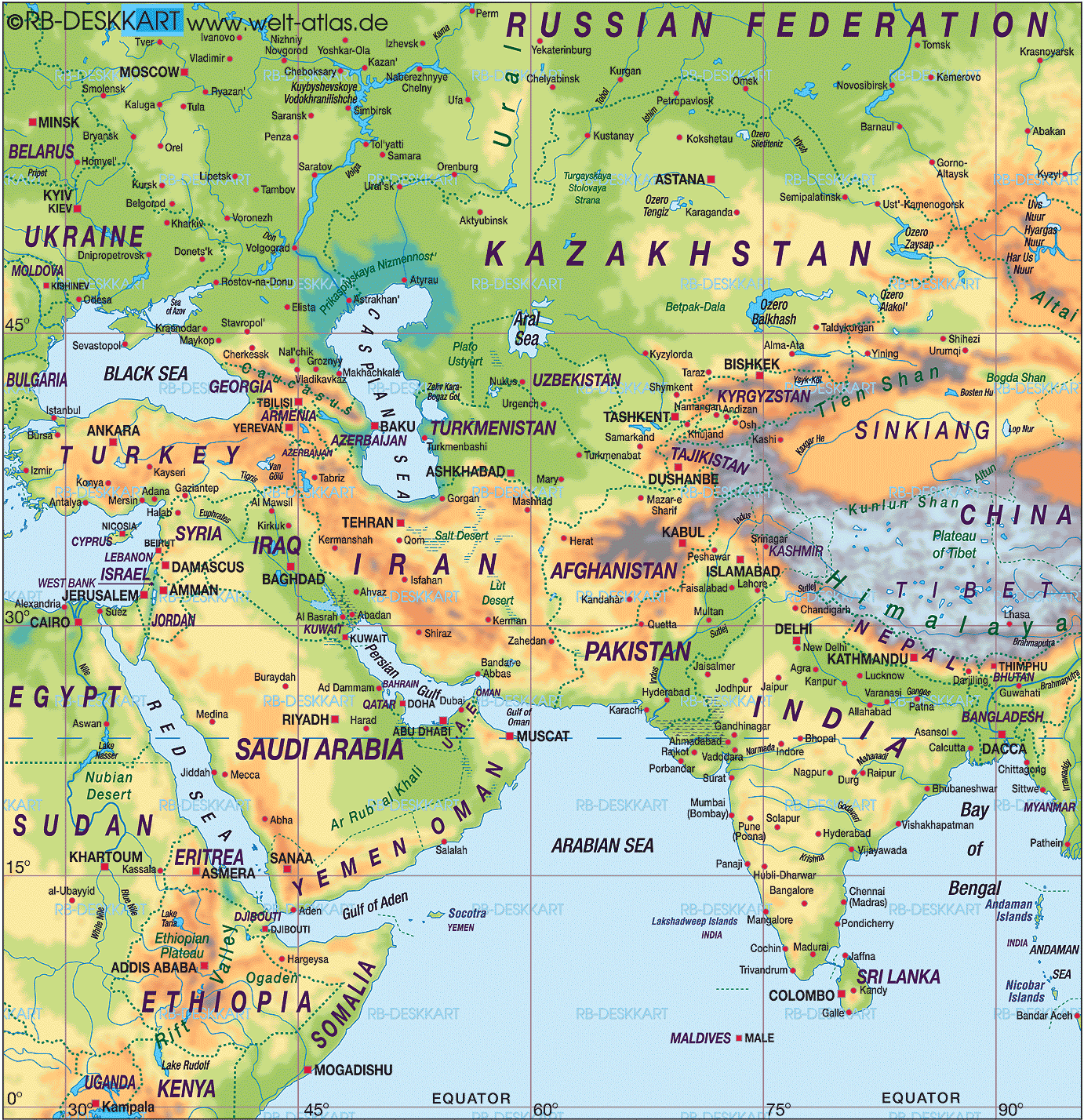
A glance at a map of Asia and the Middle East reveals a striking diversity of landscapes. From the towering Himalayas in the north to the arid deserts of the Arabian Peninsula, the region showcases a wide range of geographical features.
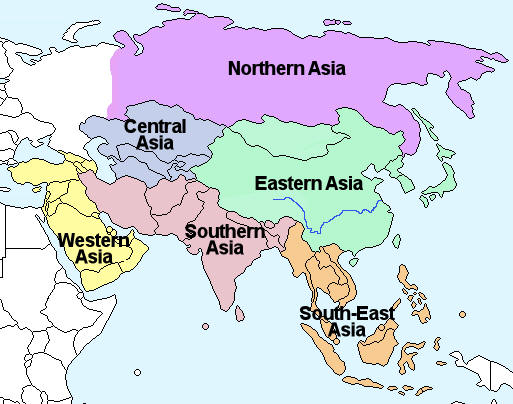
Asia:
- Central Asia: Dominated by vast steppes and deserts, Central Asia houses the towering Tian Shan and Pamir mountain ranges. Countries like Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan are located in this region.
- East Asia: Characterized by fertile plains, mountainous regions, and coastal areas, East Asia encompasses countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. The region is home to major rivers like the Yangtze and Yellow River, vital for agriculture and transportation.
- Southeast Asia: A region of diverse landscapes, including rainforests, islands, and peninsulas, Southeast Asia comprises countries like Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia. Its strategic location along major trade routes has contributed to its economic development.
- South Asia: Known for its vast plains, the Himalayas, and the Indian subcontinent, South Asia encompasses countries like India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. The Indus River and Ganges River are crucial to the region’s agriculture and cultural history.
- West Asia: Often referred to as the Middle East, West Asia is characterized by deserts, mountains, and coastal areas. Countries like Turkey, Iran, and Saudi Arabia are located in this region. The region is home to major oil reserves and strategic waterways like the Suez Canal.
The Middle East:
- Arabian Peninsula: The largest peninsula in the world, the Arabian Peninsula is dominated by deserts and mountains. It is home to major oil producers like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Levant: Located on the eastern Mediterranean coast, the Levant encompasses countries like Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan. It is known for its rich history and cultural heritage, with ancient civilizations leaving their mark on the region.
- Mesopotamia: Situated between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Mesopotamia is considered the cradle of civilization. Countries like Iraq and Kuwait are located in this region, with a rich history dating back thousands of years.
Beyond Physical Features: The Importance of Political Boundaries
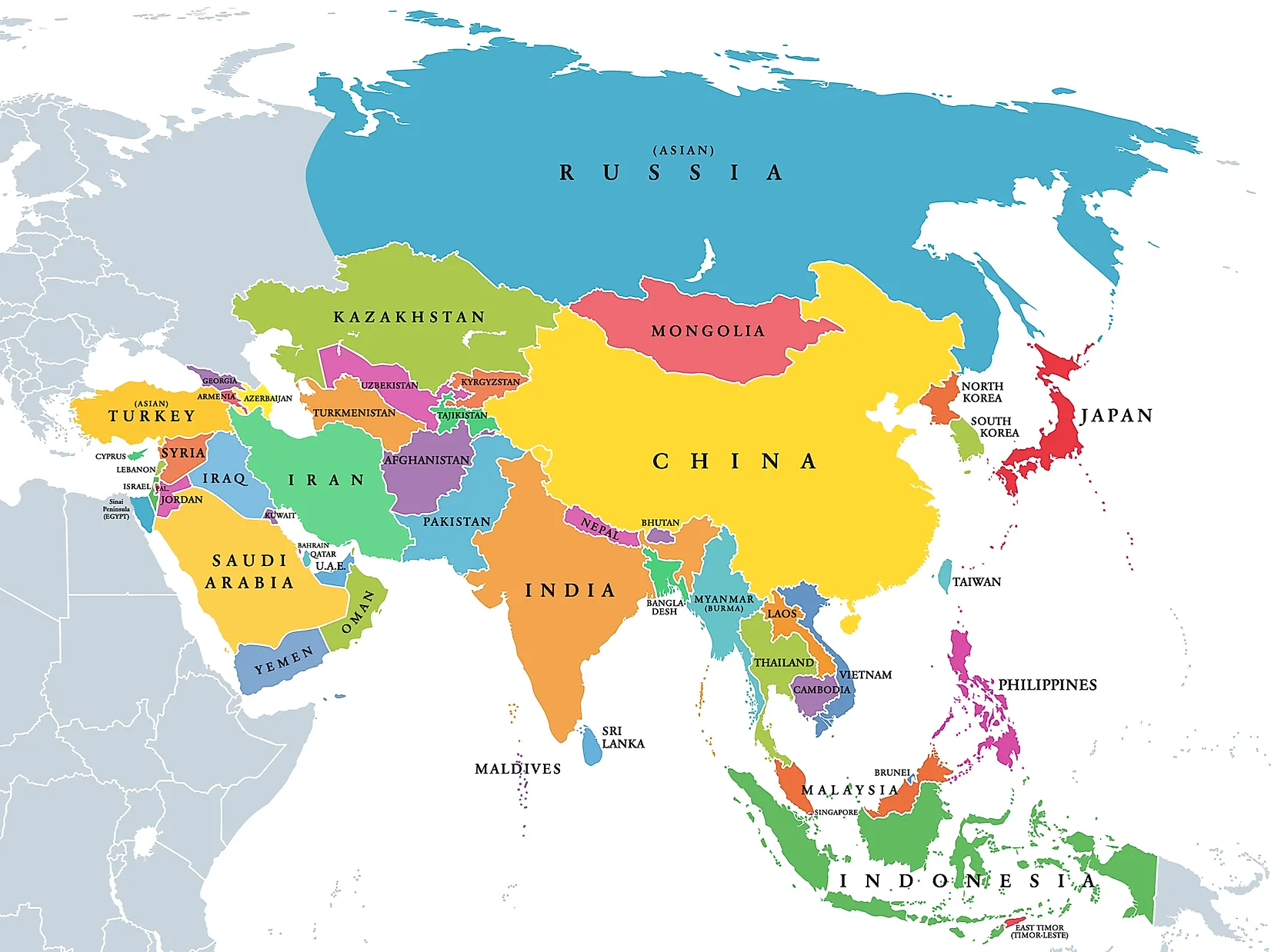
While geographical features are essential for understanding the region, political boundaries are equally crucial. The map of Asia and the Middle East showcases a complex tapestry of nations, each with its unique history, culture, and political system.
Asia:
- China: The largest country in Asia, China is a major economic and political power. Its vast size and diverse population present unique challenges and opportunities.
- India: The second-most populous country in the world, India is a democracy with a vibrant economy and a complex social structure.
- Japan: A technologically advanced nation, Japan is a significant player in the global economy. Its unique culture and history make it a fascinating study.
- South Korea: A rapidly developing economy, South Korea is known for its technological advancements and its cultural influence.
- Indonesia: The largest archipelago nation in the world, Indonesia is a diverse country with a rich cultural heritage.
The Middle East:
- Saudi Arabia: The world’s largest oil exporter, Saudi Arabia is a significant player in global energy markets. Its political and religious influence extends beyond its borders.
- Iran: A country with a long history and a complex political system, Iran is a major regional power with significant influence in the Middle East.
- Turkey: A strategically important country located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Turkey bridges the two continents and plays a vital role in regional security.
- Israel: A nation with a complex history and a unique political system, Israel has been at the center of regional conflicts and has a significant impact on the Middle East.
Understanding the Interconnectedness: A Complex Web of Relationships
The map of Asia and the Middle East is not just a collection of countries; it represents a complex web of interconnected relationships. These relationships are shaped by factors such as trade, migration, shared history, and political alliances.
- Trade Routes: The region has long been a crucial hub for trade, with ancient routes connecting East and West. The Silk Road, a historic trade route, played a significant role in the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. Today, the region remains a vital center for global trade, with major shipping lanes and trade agreements connecting its nations.
- Migration: The region has witnessed significant migration patterns throughout history. From the movement of nomadic tribes in ancient times to the contemporary flow of refugees and economic migrants, migration has shaped the region’s demographics and cultural landscape.
- Shared History: Many nations in the region share a common history, with ancient civilizations leaving their mark on the cultural landscape. The spread of Islam, the rise and fall of empires, and the impact of colonialism have shaped the region’s history and its current political realities.
- Political Alliances: The region is characterized by a complex network of political alliances and rivalries. These alliances are often based on shared interests, historical ties, and geopolitical considerations.
The Importance of Geographical Knowledge
Understanding the map of Asia and the Middle East is crucial for comprehending the region’s complexities and navigating its challenges. It provides a framework for analyzing its diverse cultures, landscapes, and political systems. This knowledge is essential for:
- International Relations: Diplomats, policymakers, and scholars need a deep understanding of the region’s geography to navigate international relations and address regional issues effectively.
- Business: Businesses operating in the region need to understand the local context, including the cultural nuances, legal frameworks, and infrastructure.
- Journalism: Journalists covering the region need a strong understanding of its geography to provide accurate and insightful reporting on current events.
- Education: Educators need to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the region’s geography to foster global citizenship and cultural awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the major geographical features of Asia and the Middle East?
A: The region is characterized by a diverse range of landscapes, including mountains, deserts, plains, rivers, and coastal areas. Some of the prominent features include the Himalayas, the Arabian Peninsula, the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, and the eastern Mediterranean coast.
Q2: What are the major political entities in the region?
A: The region is home to a diverse array of nations, including China, India, Japan, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, and Israel, each with its unique history, culture, and political system.
Q3: What are the key factors shaping the region’s interconnectedness?
A: Trade routes, migration, shared history, and political alliances play a crucial role in connecting the nations of Asia and the Middle East.
Q4: Why is understanding the map of Asia and the Middle East important?
A: This knowledge is essential for navigating international relations, conducting business, providing accurate journalism, and educating future generations about the region’s complexities.
Tips for Understanding the Map
- Study the map regularly: Familiarize yourself with the region’s countries, major cities, and geographical features.
- Use online resources: Explore interactive maps and online atlases to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s geography.
- Read books and articles: Engage with scholarly works and journalistic accounts to learn about the region’s history, culture, and politics.
- Travel to the region: If possible, visit the region to experience its diverse landscapes and cultures firsthand.
Conclusion
The map of Asia and the Middle East is a window into a world of diverse cultures, landscapes, and geopolitical realities. Understanding its complexities is essential for navigating the region’s challenges and appreciating its interconnectedness. By studying the map, engaging with its diverse peoples, and embracing its rich history, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this vibrant and influential region of the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview of Asia and the Middle East: Understanding the Region’s Complexities. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!