A Geographic Overview of Southeast Asia: A Region of Diversity and Interconnectivity
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of Southeast Asia: A Region of Diversity and Interconnectivity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of Southeast Asia: A Region of Diversity and Interconnectivity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of Southeast Asia: A Region of Diversity and Interconnectivity
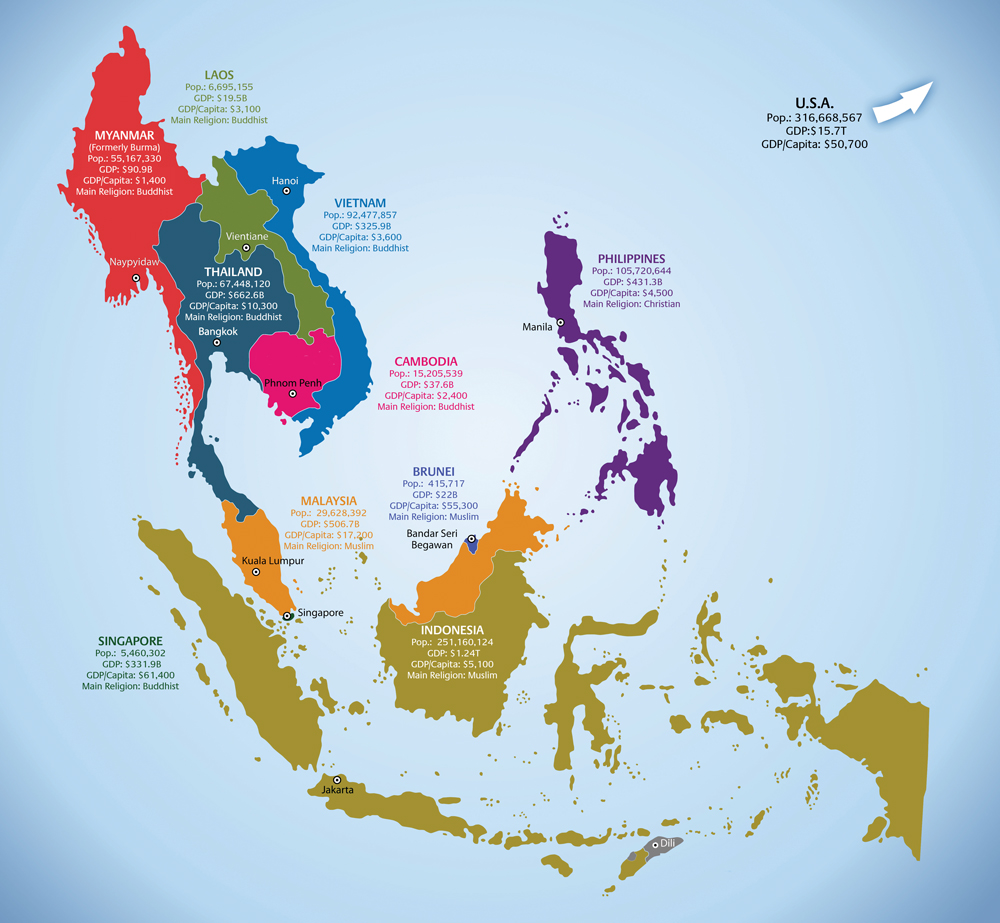
Southeast Asia, a dynamic and vibrant region nestled between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, comprises eleven countries: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste, and Vietnam. This diverse region, characterized by its rich history, cultural tapestry, and strategic geographic location, holds immense significance in the global landscape. Understanding the geographical layout of Southeast Asia is crucial for appreciating its unique complexities and its role in the world.
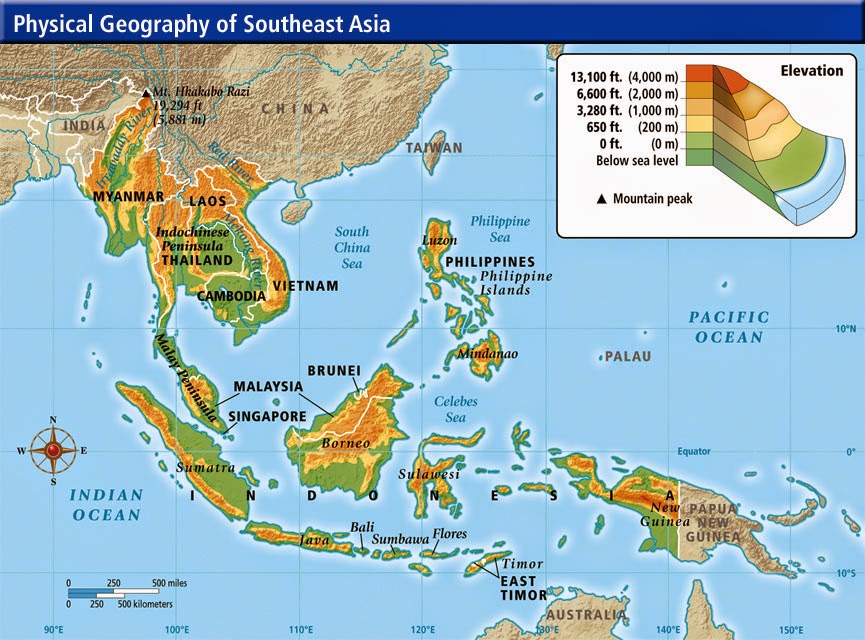
A Visual Representation: The Map of Southeast Asia
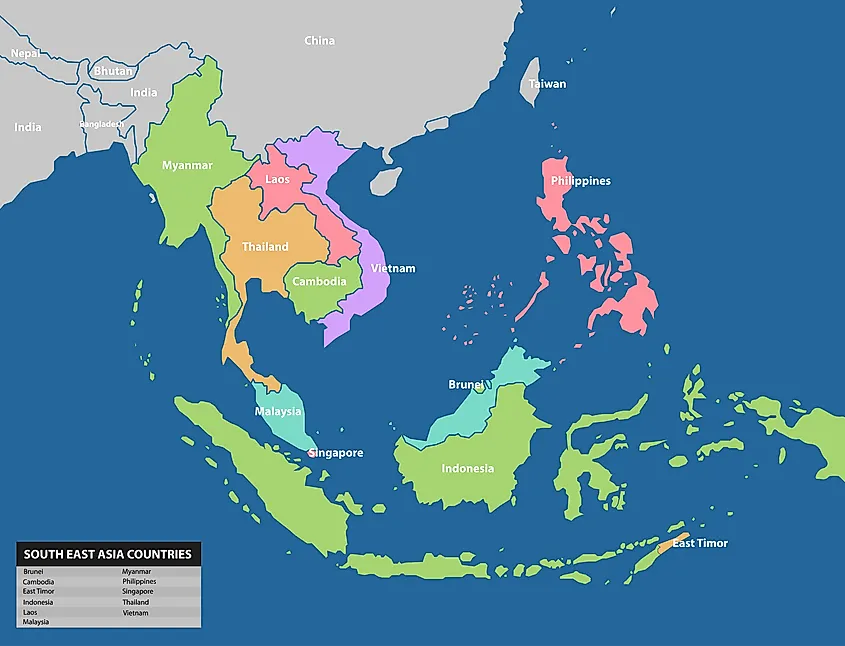
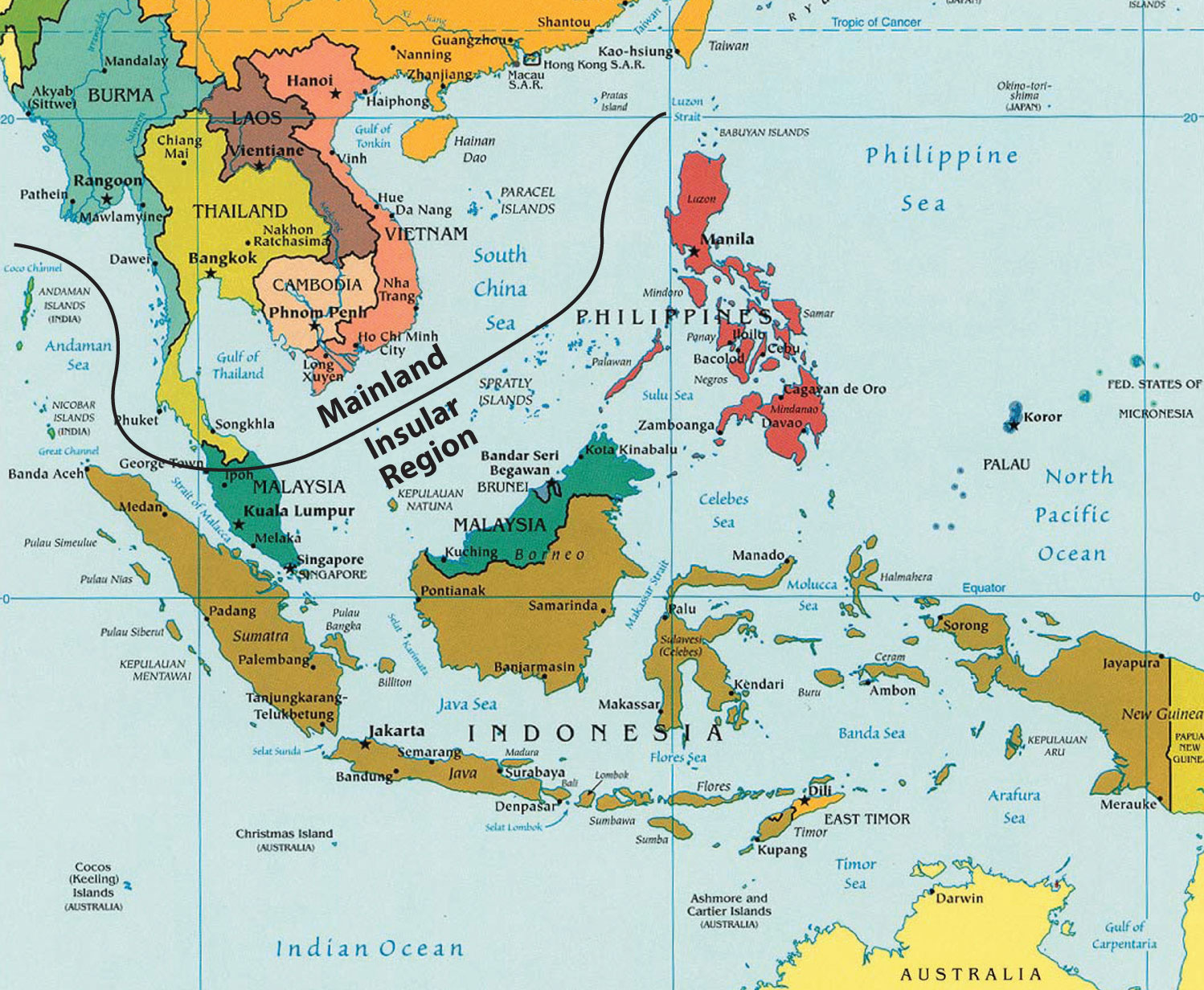
The map of Southeast Asia provides a fundamental framework for comprehending the region’s spatial relationships and understanding its diverse landscapes. The map reveals a region divided into two distinct geographical sub-regions: Mainland Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia.
Mainland Southeast Asia: This sub-region encompasses the countries of Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. It is characterized by its vast plains, fertile river valleys, and mountainous terrains. The Mekong River, one of the longest rivers in the world, flows through this region, serving as a vital artery for transportation, agriculture, and commerce.
Insular Southeast Asia: This sub-region comprises the countries of Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei, Singapore, Philippines, and Timor-Leste. It is characterized by a multitude of islands, ranging from the massive island of Borneo to the numerous smaller islands that dot the region. The archipelago of Indonesia, the largest archipelago in the world, is a defining feature of Insular Southeast Asia.
Understanding the Importance of the Map
The map of Southeast Asia serves as a crucial tool for:
-
Visualizing the Region’s Spatial Relationships: The map allows for a clear understanding of the proximity and interconnectedness of the countries within the region. This interconnectedness is evident in the shared histories, cultural influences, and economic ties that bind these nations.
-
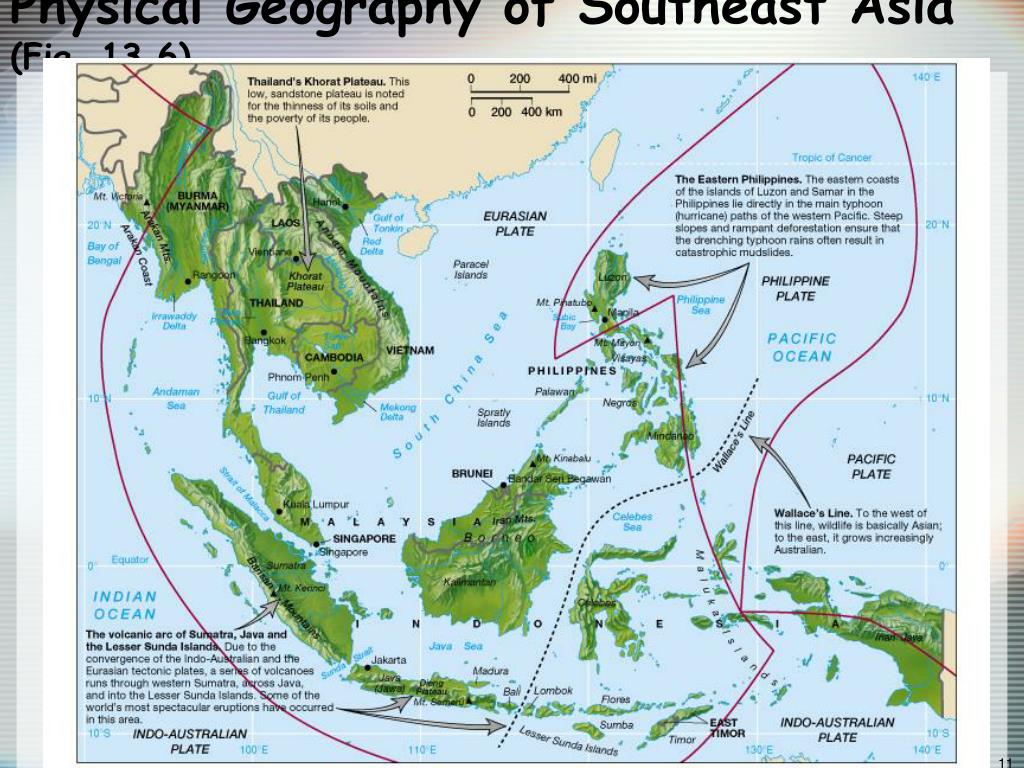
Understanding the Region’s Diverse Landscapes: The map highlights the region’s varied topography, ranging from towering mountain ranges to vast lowlands, from dense rainforests to fertile river deltas. This diverse landscape plays a significant role in shaping the region’s natural resources, agricultural practices, and cultural identities.
-
Analyzing the Region’s Strategic Location: The map showcases Southeast Asia’s location at the crossroads of major trade routes, connecting Asia with the rest of the world. This strategic position has historically played a crucial role in shaping the region’s economic development and political dynamics.
-
Exploring the Region’s Cultural Diversity: The map provides a visual representation of the region’s diverse cultural landscapes. From the ancient temples of Angkor Wat in Cambodia to the bustling streets of Singapore, the map helps us visualize the cultural richness that defines Southeast Asia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Map of Southeast Asia
Q1: What are the main physical features of Southeast Asia?
A: Southeast Asia is characterized by a diverse range of physical features, including:
- Mountain Ranges: The region is home to several mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, the Annamite Range, and the Barisan Mountains.
- River Systems: Major rivers like the Mekong, Irrawaddy, and Chao Phraya flow through the region, providing vital water resources and serving as important transportation routes.
- Islands: The region is dotted with numerous islands, ranging from the large islands of Borneo and Sumatra to the smaller islands scattered throughout the region.
- Rainforests: Southeast Asia is home to extensive rainforests, particularly in Indonesia, Malaysia, and Borneo. These rainforests are rich in biodiversity and play a crucial role in regulating the global climate.
Q2: What are the main cultural influences in Southeast Asia?
A: Southeast Asia has been shaped by a confluence of cultural influences, including:
- Indigenous Cultures: The region is home to a wide array of indigenous cultures, each with its own distinct traditions, languages, and beliefs.
- Indian Influences: Indian influences are evident in the region’s religions, languages, and art forms.
- Chinese Influences: Chinese influences have been significant, particularly in trade, cuisine, and architecture.
- Western Influences: Western influences have become increasingly prominent in recent decades, particularly in the areas of technology, education, and culture.
Q3: What are the main economic activities in Southeast Asia?
A: The economies of Southeast Asian countries are diverse, but some key economic activities include:
- Agriculture: Agriculture remains a significant sector in many Southeast Asian countries, with rice, rubber, and palm oil being major crops.
- Tourism: Tourism is a major industry in Southeast Asia, drawing visitors from around the world to its beautiful beaches, ancient temples, and vibrant cultures.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing is an important sector in some countries, particularly in Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand.
- Trade: Southeast Asia is a major hub for international trade, with its strategic location facilitating trade between Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Southeast Asia
- Study the Map Regularly: Regularly studying the map can help you become familiar with the region’s geography and the locations of its various countries.
- Use Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including interactive maps and satellite imagery, can enhance your understanding of Southeast Asia’s geography.
- Explore the Region’s History: Understanding the region’s history can provide valuable context for interpreting the map and understanding the current political and economic landscape.
- Travel to Southeast Asia: Traveling to Southeast Asia is an excellent way to experience the region’s diverse cultures and landscapes firsthand.
Conclusion: The Map as a Gateway to Understanding
The map of Southeast Asia is more than just a static representation of geographical features. It serves as a gateway to understanding the region’s complex history, its vibrant cultures, its diverse landscapes, and its strategic importance in the global arena. By engaging with the map and exploring its intricacies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and dynamism of Southeast Asia, a region that continues to captivate and inspire the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of Southeast Asia: A Region of Diversity and Interconnectivity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!