A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Significance
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Significance

Asia, the largest and most populous continent on Earth, is a tapestry of vibrant cultures, diverse landscapes, and rich history. Its vast expanse encompasses 49 countries, each with its unique identity and contribution to the global stage. Understanding the geography and cultural diversity of Asia is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the modern world.
A Geographical Overview:
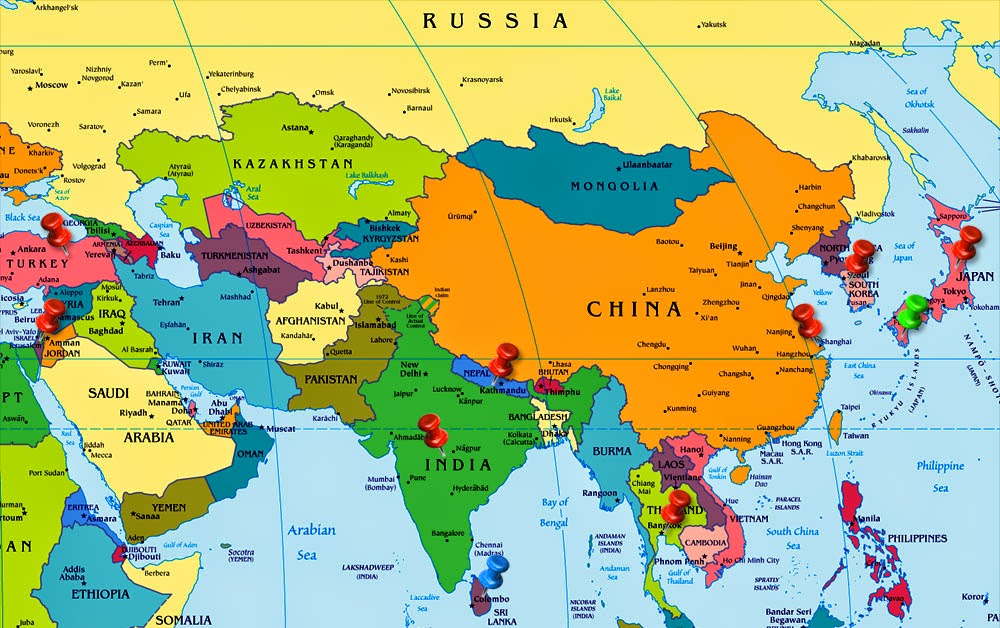
Asia’s sprawling geography is characterized by its remarkable diversity, encompassing towering mountain ranges, vast deserts, lush rainforests, and fertile plains. The continent is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Indian Ocean to the south, and Europe to the west.
Major Geographic Features:
- The Himalayas: This majestic mountain range, home to the world’s highest peak, Mount Everest, forms a natural barrier between South Asia and Central Asia.
- The Tibetan Plateau: Known as the "Roof of the World," this high-altitude plateau is a source of major rivers, including the Yangtze, Yellow, and Mekong.
- The Gobi Desert: This vast, arid region in Central Asia is a stark contrast to the lush landscapes found elsewhere in Asia.
- The Indus River Valley: This fertile plain in South Asia is home to one of the world’s oldest civilizations.
- The Mekong River Delta: This densely populated region in Southeast Asia is a vital agricultural area and a hub for trade.
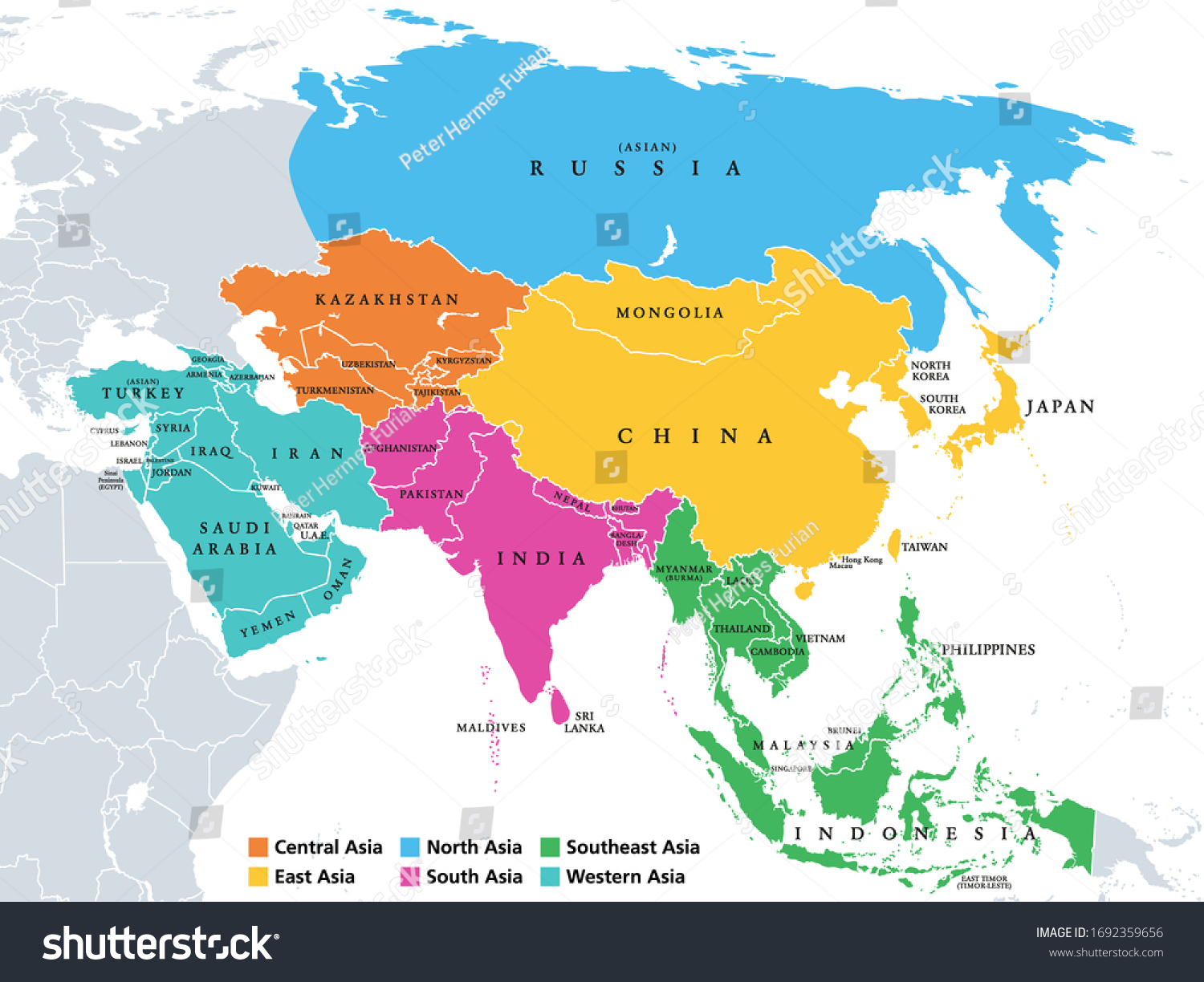
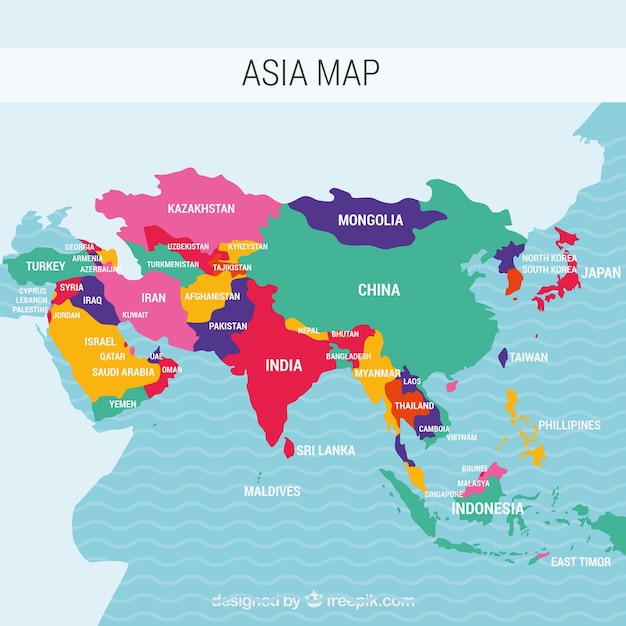
Key Geographical Regions:
- East Asia: This region includes China, Japan, South Korea, North Korea, and Mongolia. It is characterized by its advanced economies, technological innovation, and cultural influence.
- Southeast Asia: This region encompasses countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, and the Philippines. It is known for its diverse cultures, tropical landscapes, and growing economies.
- South Asia: This region includes India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal. It is home to a rich history, vibrant cultures, and a rapidly developing economy.
- Central Asia: This landlocked region includes Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan. It is known for its vast steppes, rich mineral resources, and historical Silk Road connections.
- West Asia: This region, also known as the Middle East, includes countries like Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and Israel. It is a region of significant historical, cultural, and geopolitical importance.
Cultural Diversity:
Asia’s cultural diversity is as vast as its geography. From the ancient traditions of India to the modern dynamism of Japan, each country boasts unique customs, languages, religions, and artistic expressions.
Major Religions:
- Buddhism: Originating in India, Buddhism spread throughout East Asia and Southeast Asia, influencing art, philosophy, and daily life.
- Islam: The dominant religion in West Asia, Islam also has a strong presence in South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Central Asia.
- Hinduism: This ancient religion originated in India and is practiced by a majority of the population in South Asia.
- Christianity: With a significant presence in the Philippines, Armenia, and East Timor, Christianity has also left its mark on the cultural landscape of Asia.
Language Families:
Asia is home to a wide array of language families, including:
- Indo-European: This family includes languages like Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, and Persian.
- Sino-Tibetan: This family includes Mandarin Chinese, Tibetan, and Burmese.
- Austronesian: This family includes languages like Malay, Indonesian, and Tagalog.
- Altaic: This family includes languages like Turkish, Mongolian, and Korean.
Economic and Political Significance:
Asia is a powerhouse in the global economy, boasting some of the world’s largest economies and fastest-growing markets. The continent is also home to a diverse range of political systems, from democracies to monarchies to communist states.
Major Economies:
- China: The world’s second-largest economy, China is a major player in global trade and manufacturing.
- Japan: Known for its technological advancements and strong manufacturing base, Japan is a leading economic power in Asia.
- India: The world’s sixth-largest economy, India is experiencing rapid economic growth and is a hub for technology and outsourcing.
- South Korea: A technological powerhouse, South Korea is a major exporter of electronics and automobiles.
Political Systems:
- Democracy: Countries like India, Japan, and South Korea have democratic systems of government.
- Monarchy: Countries like Thailand, Malaysia, and Bhutan are constitutional monarchies.
- Communist State: China and North Korea are communist states.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Asia faces a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. However, the continent also presents significant opportunities for economic growth, technological innovation, and cultural exchange.
Environmental Challenges:
- Air pollution: Many Asian cities struggle with severe air pollution, impacting public health and the environment.
- Deforestation: Rapid economic growth has led to widespread deforestation, threatening biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Water scarcity: Many parts of Asia face water scarcity, particularly in arid regions and densely populated areas.
Economic Opportunities:
- Growing middle class: Asia’s rapidly growing middle class is driving consumer demand and creating new markets.
- Technological innovation: Asia is a hub for technological innovation, with countries like China and South Korea leading the way in areas like artificial intelligence and renewable energy.
- Infrastructure development: Investment in infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and ports, is creating new opportunities for economic growth.
Cultural Exchange:
- Tourism: Asia is a popular destination for tourists from around the world, fostering cultural exchange and understanding.
- Education: Asian universities are attracting students from all over the globe, promoting international collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Arts and culture: Asian art, music, and literature are increasingly gaining recognition on the global stage, enriching cultural diversity.
Conclusion:
Asia is a continent of immense diversity, both geographically and culturally. Its vast landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures make it a fascinating region to explore. Understanding Asia’s geography, cultural nuances, and economic significance is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the modern world. As the continent continues to grow and evolve, its impact on the global stage will only continue to increase.
FAQs
Q: What is the largest country in Asia?
A: Russia is the largest country in Asia by land area, spanning over 17 million square kilometers.
Q: What is the most populous country in Asia?
A: China is the most populous country in Asia, with a population of over 1.4 billion people.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Asia?
A: The major languages spoken in Asia include Mandarin Chinese, Hindi, Bengali, Urdu, Japanese, and Arabic.
Q: What are some of the most popular tourist destinations in Asia?
A: Popular tourist destinations in Asia include the Taj Mahal in India, the Great Wall of China, Angkor Wat in Cambodia, and the Forbidden City in China.
Q: What are some of the key challenges facing Asia?
A: Key challenges facing Asia include poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, political instability, and religious tensions.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for economic growth in Asia?
A: Opportunities for economic growth in Asia include the growing middle class, technological innovation, infrastructure development, and increasing trade with other countries.
Tips
- Use a map: A map is an essential tool for understanding the geography of Asia.
- Research different countries: Each country in Asia has its unique history, culture, and challenges.
- Learn about different religions: Asia is home to a wide range of religions, each with its own beliefs and practices.
- Explore different languages: Learning a few phrases in a local language can enhance your travel experience.
- Stay informed about current events: Asia is a dynamic region with ongoing political and economic developments.
Conclusion
Asia is a continent of immense diversity and significance. Its vast geography, rich history, and vibrant cultures make it a fascinating region to explore. Understanding Asia’s complexities is crucial for comprehending the interconnectedness of the global community.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!