A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Interconnectedness
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Interconnectedness
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Interconnectedness. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Interconnectedness

Asia, the largest and most populous continent on Earth, is a sprawling tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories. Its immense size and geographical complexity have shaped its political, economic, and social fabric, making it a region of immense global significance. This article delves into the intricate geography of Asia, exploring its diverse regions, major countries, and the unique characteristics that define its multifaceted identity.
A Continent of Extremes:
Asia’s geographical diversity is unparalleled. From the towering Himalayas in the north to the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, from the vast steppes of Central Asia to the fertile plains of the Indus River Valley, the continent encompasses a spectrum of landscapes. Its varied topography has given rise to diverse climates, ranging from the frigid winters of Siberia to the scorching deserts of the Arabian Peninsula. This diversity has fostered a unique array of flora and fauna, making Asia a global biodiversity hotspot.
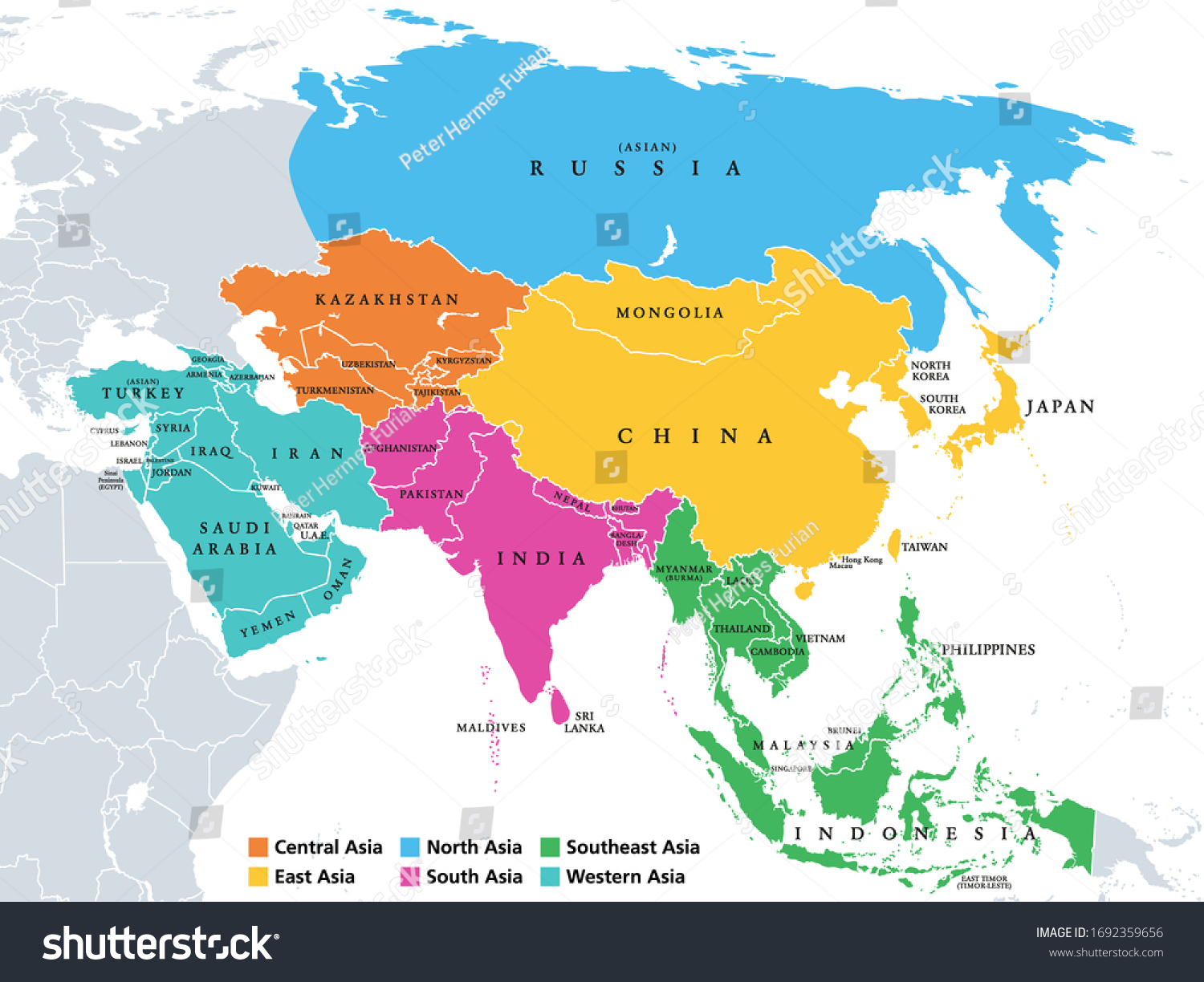
Regional Divisions: A Framework for Understanding:
To navigate the vastness of Asia, it is helpful to divide the continent into distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics:
-
Northeast Asia: This region, encompassing China, Japan, North Korea, and South Korea, is characterized by its advanced economies, technological prowess, and vibrant cultural traditions. The region is home to some of the world’s largest cities and industrial centers, contributing significantly to global trade and innovation.
-
Southeast Asia: Comprising countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, and the Philippines, Southeast Asia is a region of immense cultural and linguistic diversity. Its tropical climate, fertile lands, and strategic location have made it a hub for agriculture, trade, and tourism.
-
South Asia: This region, encompassing India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, is known for its ancient civilizations, rich cultural heritage, and significant economic growth. The region is home to the Indus River Valley, a cradle of civilization, and its diverse landscapes range from the Himalayas to the lush plains of the Ganges River.
-
Central Asia: This landlocked region, comprising countries like Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, is characterized by its vast steppes, arid deserts, and rich mineral resources. Central Asia has historically served as a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, connecting East and West.
-
West Asia: Also known as the Middle East, this region includes countries like Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia. It is characterized by its vast deserts, rich oil reserves, and its historical significance as the birthplace of major religions like Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
A Mosaic of Countries: Unique Identities and Shared Challenges:
Within these regional frameworks, Asia is home to a diverse array of countries, each with its own unique history, culture, and political system. Some of the major Asian countries include:
-
China: The world’s most populous country, China has a rich history and a rapidly growing economy. It is a major player in global trade and manufacturing, and its influence extends across the continent and beyond.
-
India: The world’s second most populous country, India is a vibrant democracy with a rapidly developing economy. It is known for its ancient civilizations, diverse cultures, and its burgeoning technology sector.
-
Japan: An economic powerhouse, Japan is known for its technological innovation, high-quality manufacturing, and its rich cultural traditions. It is a major player in global trade and finance.
-
Russia: Spanning both Europe and Asia, Russia is the largest country in the world. It is known for its vast natural resources, its history as a superpower, and its complex political system.
-
Indonesia: The world’s largest archipelago nation, Indonesia is known for its diverse cultures, stunning landscapes, and its growing economy. It is a significant producer of natural resources and a major player in Southeast Asian politics.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Asia faces numerous challenges, including rapid urbanization, environmental degradation, and social inequalities. However, the continent also presents immense opportunities for economic growth, technological advancement, and social progress.
-
Urbanization: Asia is experiencing rapid urbanization, with millions of people moving to cities in search of better opportunities. This presents challenges for infrastructure development, housing, and environmental sustainability.
-
Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and climate change are major environmental challenges facing Asia. The continent is home to some of the world’s most polluted cities and is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
-
Social Inequalities: Despite economic growth, Asia continues to grapple with social inequalities, including poverty, gender discrimination, and lack of access to education and healthcare.
-
Economic Growth: Asia is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing trade, technological innovation, and a young and growing population.
-
Technological Advancement: Asia is a leader in technological innovation, with countries like China, Japan, and South Korea investing heavily in research and development. This technological advancement is driving economic growth and creating new opportunities for the region.
-
Social Progress: Asia is making strides in social progress, with improvements in education, healthcare, and women’s empowerment. However, more needs to be done to address social inequalities and ensure that everyone benefits from economic growth.
Conclusion:
Asia is a continent of immense diversity, complexity, and dynamism. Its geographical expanse, diverse cultures, and rapidly evolving economies make it a region of immense global significance. Understanding the geography of Asia is crucial for appreciating its unique characteristics, navigating its challenges, and harnessing its opportunities. As the continent continues to grow and evolve, its influence on the world stage will only continue to increase.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major geographic features of Asia?
A: Asia is characterized by a wide range of geographic features, including:
- Mountains: The Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, traverse the northern part of the continent. Other major mountain ranges include the Tian Shan, the Pamir Mountains, and the Hindu Kush.
- Plateaus: Asia is home to vast plateaus, such as the Tibetan Plateau, the Iranian Plateau, and the Deccan Plateau.
- Rivers: Major rivers like the Yangtze, the Yellow River, the Ganges, and the Indus flow through Asia, providing water for agriculture, transportation, and urban development.
- Deserts: Asia is home to some of the world’s largest deserts, including the Gobi Desert, the Thar Desert, and the Arabian Desert.
- Islands: Asia is home to numerous islands, including the Indonesian archipelago, the Philippines, and the Japanese archipelago.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Asia?
A: Asia is home to a diverse range of religions, including:
- Hinduism: Predominantly practiced in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- Islam: The dominant religion in West Asia, Central Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Buddhism: Originating in India, Buddhism is widely practiced in countries like China, Japan, Korea, Thailand, and Sri Lanka.
- Christianity: A significant religion in countries like the Philippines, South Korea, and East Timor.
- Confucianism: A philosophical system and ethical code that has influenced Chinese culture and society for centuries.
- Taoism: A philosophical and religious tradition that emphasizes harmony with nature and the pursuit of the Tao, or the "way."
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Asia?
A: Asia is home to a vast array of languages, with some of the most widely spoken languages including:
- Mandarin Chinese: Spoken by over 1 billion people, primarily in China.
- Hindi: The official language of India, spoken by over 600 million people.
- English: Widely spoken in many Asian countries due to its historical significance and its role in global trade and communication.
- Arabic: The official language of many countries in West Asia and North Africa.
- Bengali: The official language of Bangladesh and one of the official languages of India.
- Russian: Spoken in Russia and other parts of Central Asia.
- Japanese: Spoken in Japan and by a significant diaspora community around the world.
Q: What are the major economic sectors in Asia?
A: Asia’s economy is diverse and dynamic, with major sectors including:
- Agriculture: Agriculture remains a significant sector in many Asian countries, particularly in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
- Manufacturing: Asia is a global hub for manufacturing, with countries like China, Japan, and South Korea leading in various industries.
- Technology: Asia is a leader in technological innovation, with major technology companies based in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
- Tourism: Tourism is a significant economic sector in many Asian countries, particularly in Southeast Asia and South Asia.
- Energy: Asia is home to significant oil and gas reserves, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Russia being major producers.
Tips:
- Use a comprehensive atlas or online map resource: A detailed map of Asia is essential for understanding the continent’s geography.
- Explore the different regions: Focus on specific regions to gain a deeper understanding of their unique characteristics and the challenges they face.
- Research individual countries: Learn about the history, culture, and current events of individual Asian countries to gain a nuanced perspective.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from different sources, including academic journals, news articles, and cultural organizations, to gain a broader understanding of Asian perspectives.
- Consider the impact of globalization: Analyze how globalization has impacted Asian societies, economies, and cultures.
Conclusion:
Asia is a continent of immense complexity and dynamism. Its diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories have shaped its political, economic, and social fabric, making it a region of immense global significance. Understanding the geography of Asia is essential for appreciating its unique characteristics, navigating its challenges, and harnessing its opportunities. As the continent continues to grow and evolve, its influence on the world stage will only continue to increase.




![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Asia: A Continent of Diversity and Interconnectedness. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!