A Comprehensive Overview of Asia: A Geographic and Political Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Overview of Asia: A Geographic and Political Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Overview of Asia: A Geographic and Political Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Overview of Asia: A Geographic and Political Landscape
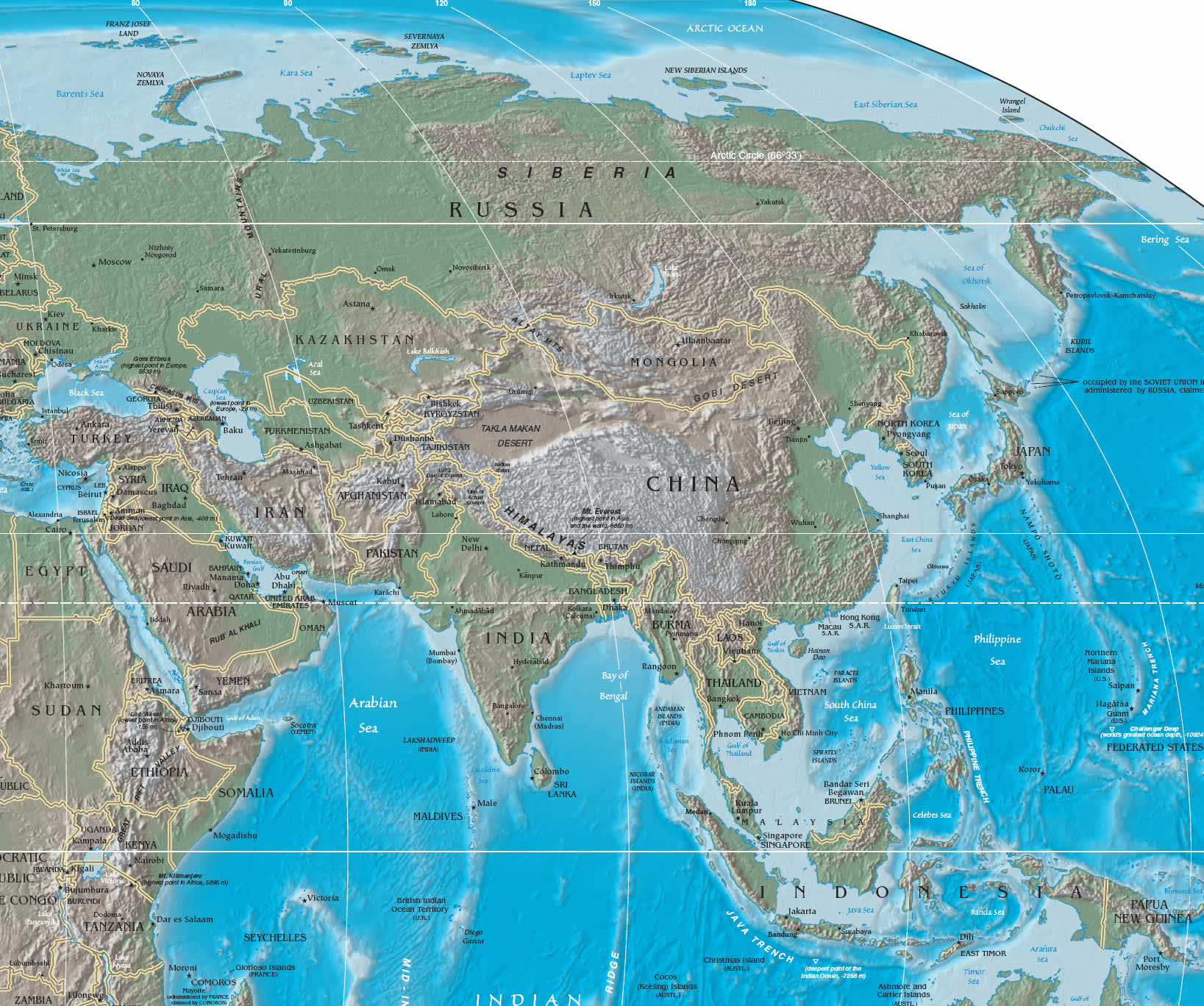
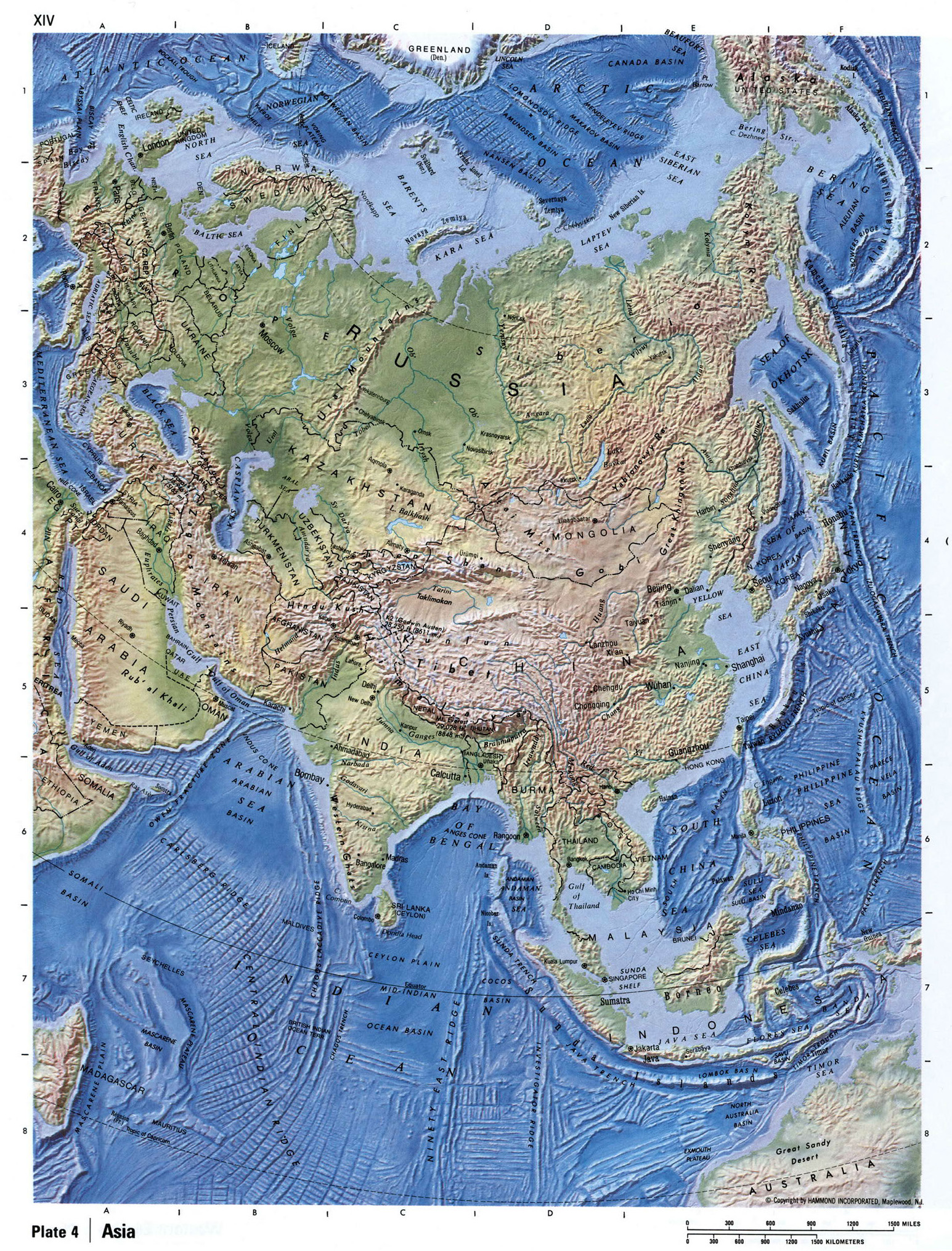
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, encompasses a vast and diverse tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and political entities. Understanding the geographical and political framework of Asia is crucial for comprehending its history, current affairs, and global significance. This article provides a detailed exploration of the Asian continent, outlining its geographical features, political divisions, and the interconnectedness of its nations.
A Geographical Tapestry: From Mountains to Seas
Asia’s geographical expanse, stretching from the eastern Mediterranean to the Pacific Ocean and from the Arctic Circle to the Indian Ocean, encompasses a staggering array of landscapes. The continent’s physical geography is characterized by towering mountain ranges, sprawling plains, fertile river valleys, vast deserts, and extensive coastlines.
The Mighty Himalayas: The Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, form a natural barrier between India and China, shaping the climate and influencing the cultural development of the region. The Himalayas are home to numerous peaks exceeding 8,000 meters, including Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak.
The Fertile Plains: The Indo-Gangetic Plain, located in northern India and Pakistan, is one of the most fertile regions in the world, supporting a dense population and a thriving agricultural sector. The fertile plains of China, such as the North China Plain and the Sichuan Basin, are similarly crucial for the country’s agricultural production.
The Vast Deserts: The Arabian Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, dominates the Arabian Peninsula, while the Gobi Desert in northern China and Mongolia is a vast expanse of arid land. These deserts pose unique challenges for human habitation and resource management.
The Diverse Coastlines: Asia’s extensive coastlines are home to numerous islands, peninsulas, and gulfs. The Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, the South China Sea, and the East China Sea are vital waterways for trade and transportation. The continent’s coastal areas are also home to diverse ecosystems, including coral reefs, mangroves, and wetlands.
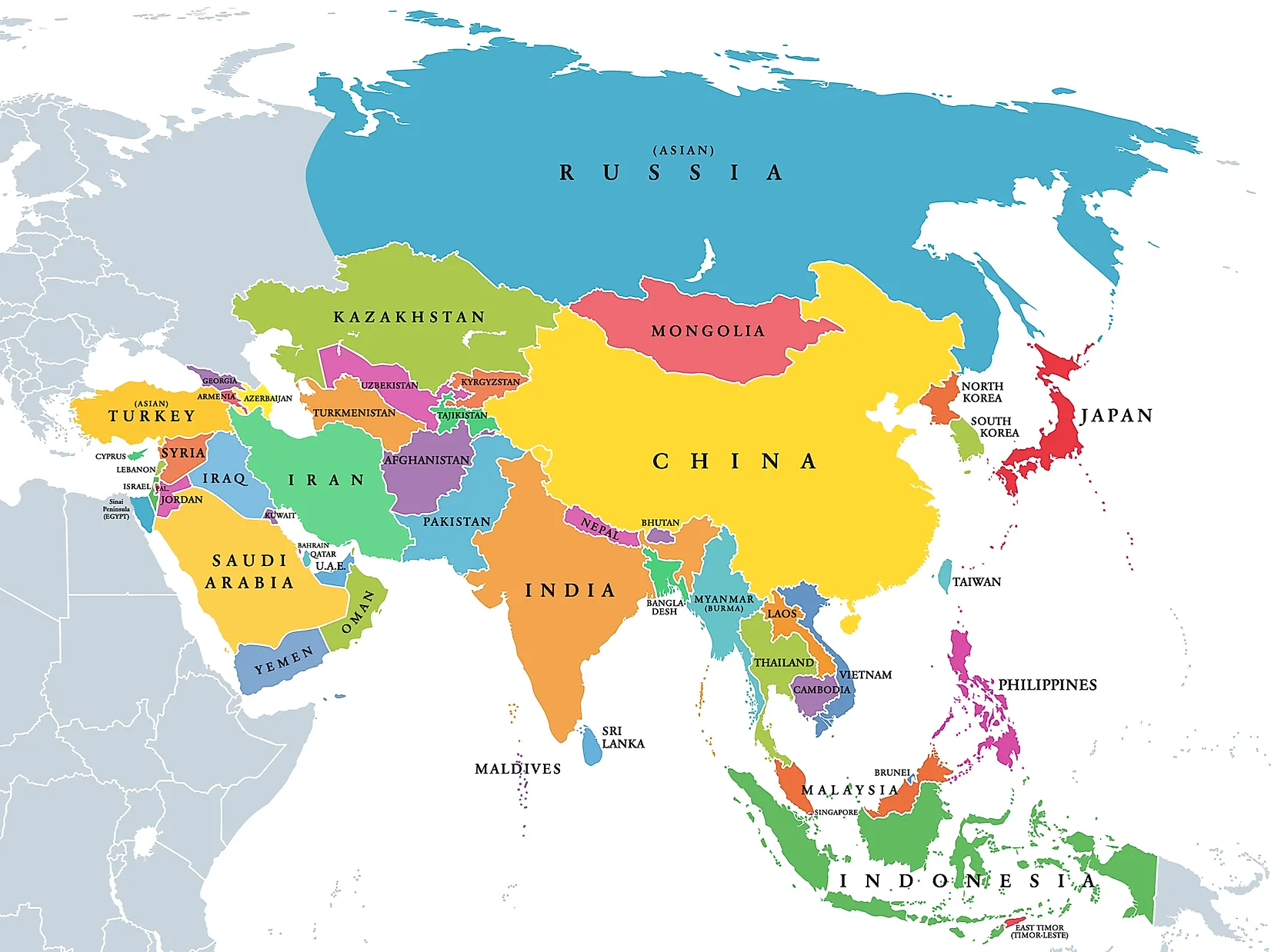
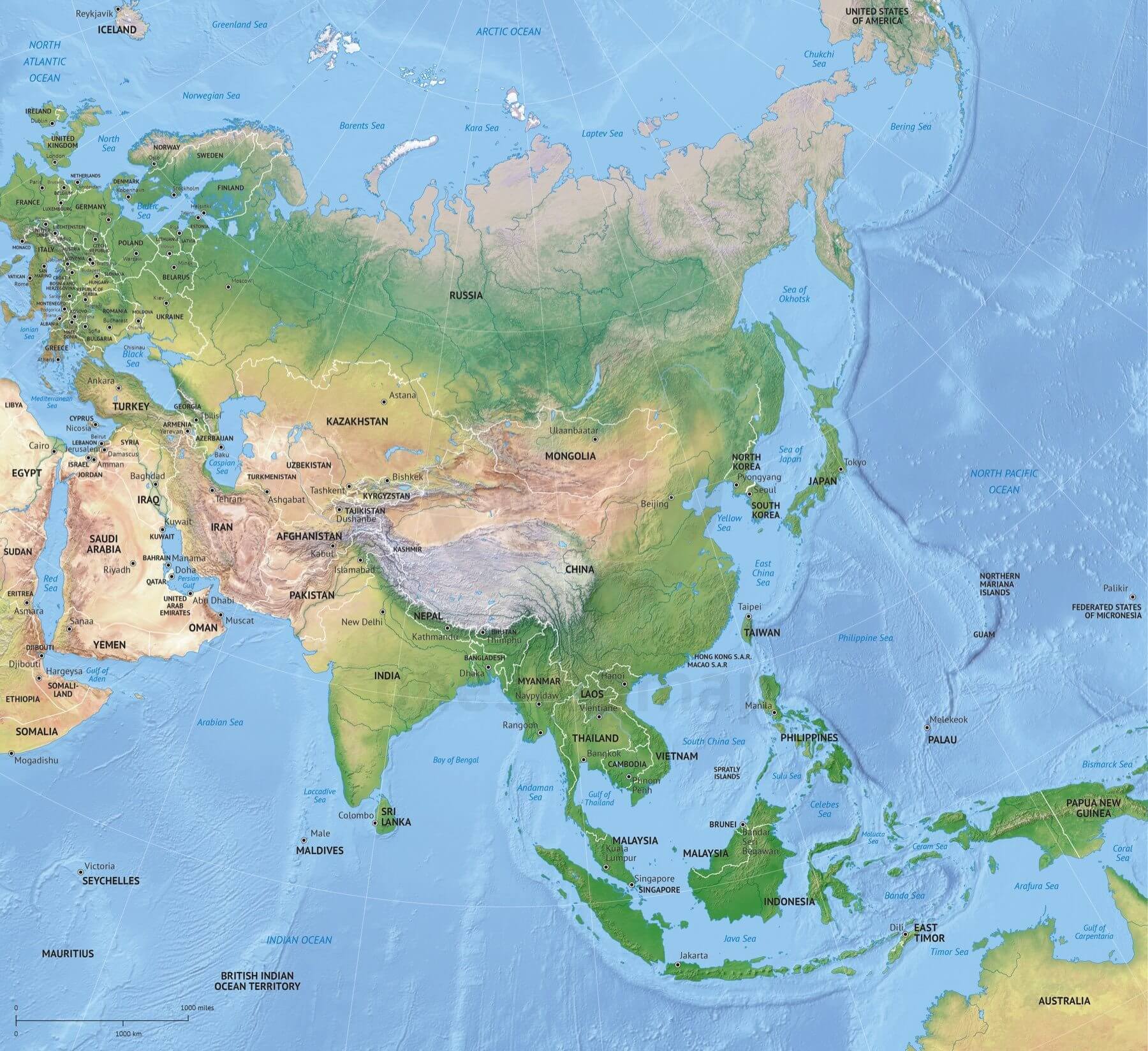
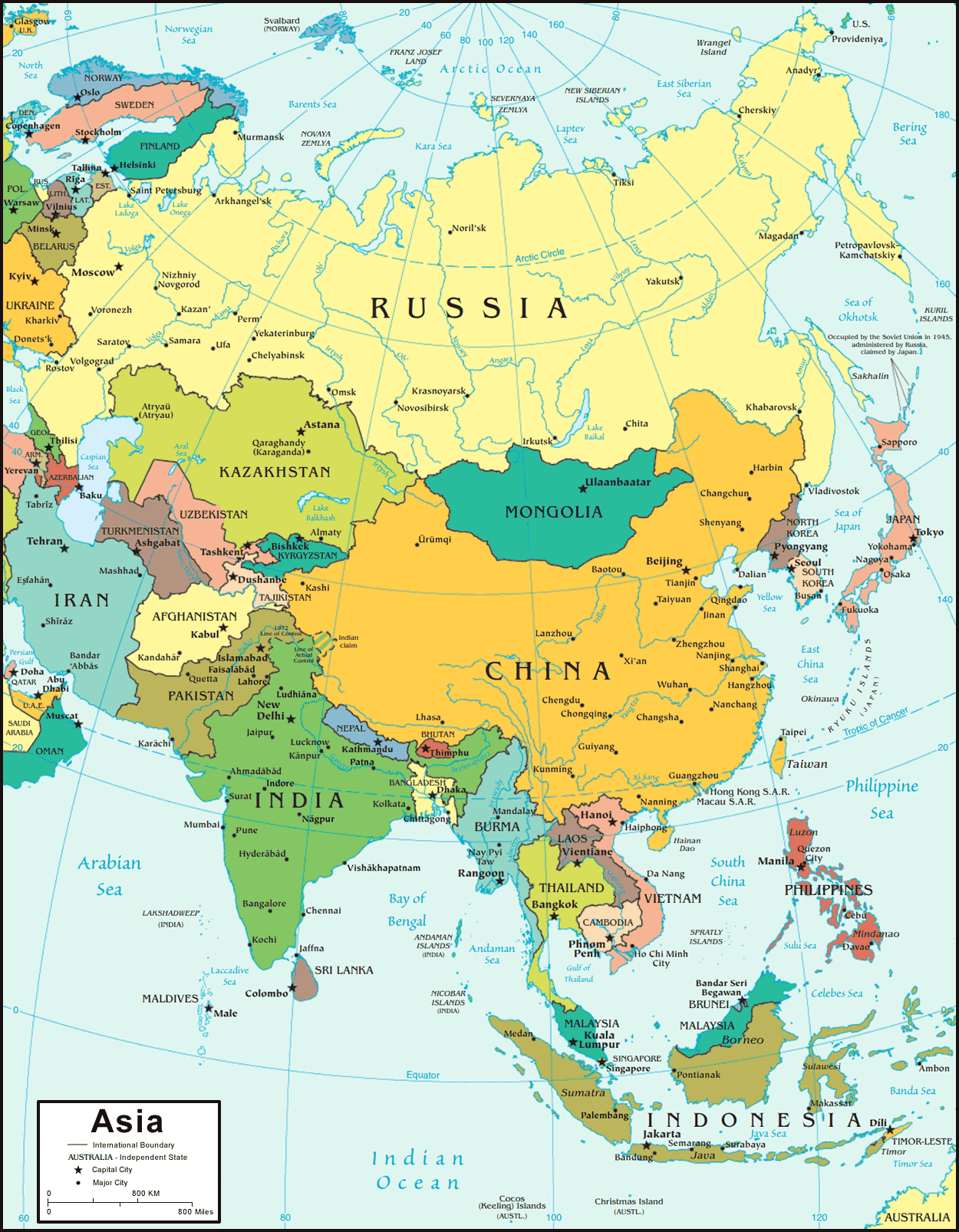
Political Divisions: A Mosaic of Nations
Asia is home to 49 sovereign states, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. The continent’s political landscape is a complex tapestry of diverse nations, ranging from large, powerful countries like China and India to smaller island nations like Singapore and the Maldives.
East Asia: This region comprises China, Japan, South Korea, North Korea, Mongolia, and Taiwan. China, the world’s most populous nation, is a major economic and military power. Japan and South Korea are highly developed economies with advanced technologies. North Korea remains a closed and isolated state.
Southeast Asia: This region includes Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Brunei. Southeast Asia is characterized by its diverse cultures, tropical climates, and significant economic growth.
South Asia: This region includes India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and the Maldives. India, the world’s second-most populous country, is a major economic and political force in the region. Pakistan and Bangladesh are also populous nations with significant challenges.
Central Asia: This region includes Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Afghanistan. Central Asia is home to vast steppes, mountain ranges, and a diverse mix of cultures.
West Asia: This region, also known as the Middle East, includes Turkey, Israel, Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates. West Asia is strategically important due to its vast oil reserves and its location at the crossroads of continents.
The Importance of Understanding Asia’s Map
A comprehensive understanding of Asia’s map is essential for several reasons:
- Global Interconnectedness: Asia plays a critical role in the global economy, politics, and culture. Its vast resources, growing economies, and diverse populations make it a key player in international affairs.
- Understanding Regional Dynamics: The map helps us understand the complex relationships between Asian countries, their shared histories, cultural exchanges, and political interactions.
- Navigating Global Challenges: Asia is facing numerous challenges, including climate change, resource scarcity, and political instability. Understanding the map helps us analyze these challenges and identify potential solutions.
- Promoting Cultural Exchange: The map provides a visual representation of Asia’s cultural diversity, fostering appreciation and understanding of different societies and traditions.
FAQs about the Map of Asia
Q: What is the largest country in Asia by land area?
A: The largest country in Asia by land area is Russia, which spans across both Europe and Asia.
Q: What is the most populous country in Asia?
A: China is the most populous country in Asia and the world.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Asia?
A: Asia is home to a wide variety of religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, and Confucianism.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Asia?
A: Asia is home to numerous languages, including Mandarin Chinese, Hindi, English, Arabic, Bengali, and Japanese.
Q: What are the major economic hubs in Asia?
A: Major economic hubs in Asia include Tokyo, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Seoul.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Asia
- Use a reliable map: Choose a map that clearly shows the boundaries of each country, major cities, and geographical features.
- Focus on key regions: Start by understanding the major regions of Asia, such as East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, Central Asia, and West Asia.
- Explore the physical geography: Pay attention to the mountains, rivers, deserts, and coastlines that shape the continent’s landscape.
- Learn about the political divisions: Understand the names and locations of the different countries in Asia and their political systems.
- Research cultural and historical connections: Explore the shared histories, cultural exchanges, and political interactions between Asian nations.
Conclusion: A Continent of Possibilities
The map of Asia is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s vastness, diversity, and interconnectedness. It reveals the intricate tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and political entities that make up this dynamic region. By studying the map and its nuances, we gain a deeper appreciation for Asia’s rich history, its current challenges, and its immense potential for the future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Overview of Asia: A Geographic and Political Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!