A Comprehensive Look at Asia: 48 Countries and a Continent of Diversity
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Asia: 48 Countries and a Continent of Diversity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Asia: 48 Countries and a Continent of Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Asia: 48 Countries and a Continent of Diversity
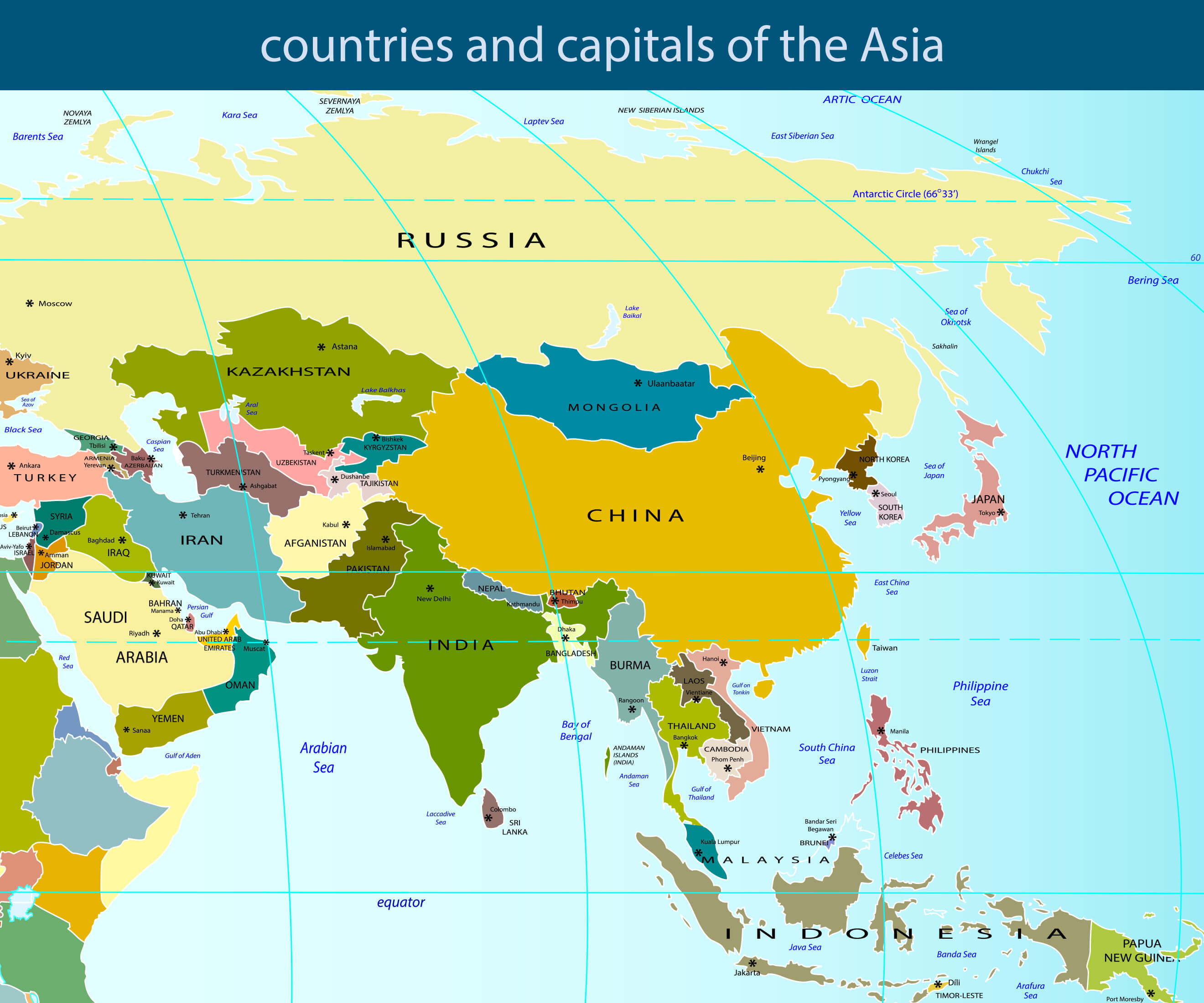
Asia, the largest and most populous continent on Earth, is a tapestry of cultures, languages, landscapes, and histories. Spanning over 44,614,000 square kilometers and home to nearly 4.7 billion people, it is a region of immense geographical and cultural significance. This article explores the intricate mosaic of Asia, focusing on the 48 countries that contribute to its multifaceted identity.
A Geographical Overview:
Asia encompasses a vast expanse, stretching from the easternmost point of the Bering Strait to the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula. Its northern boundary borders the Arctic Ocean, while its southern boundary is defined by the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. The continent’s diverse landscape includes towering mountain ranges, expansive deserts, fertile plains, and dense rainforests.
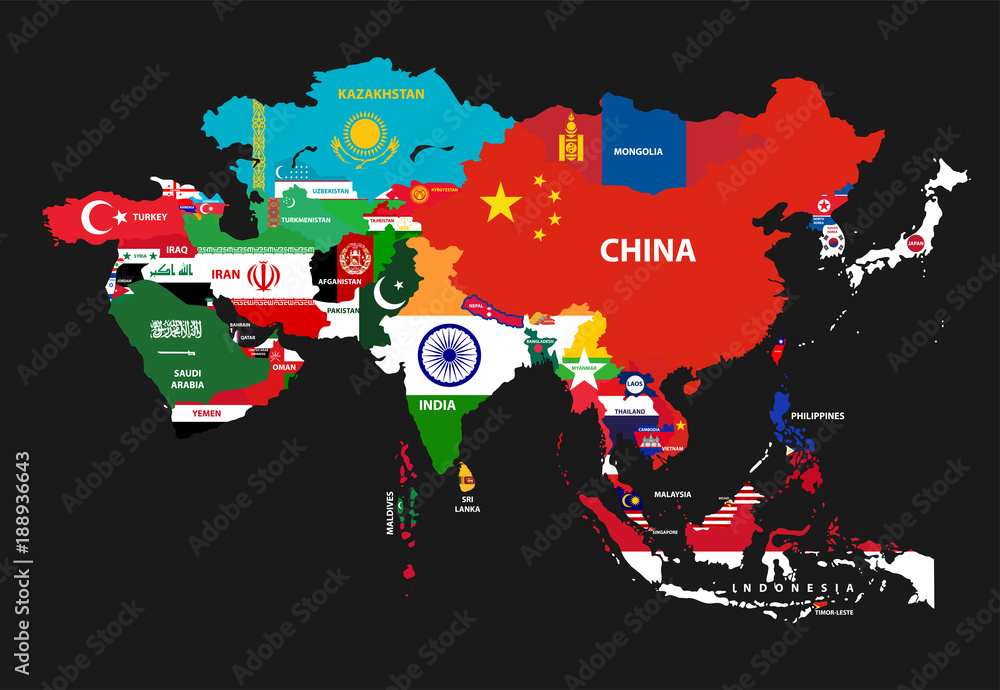
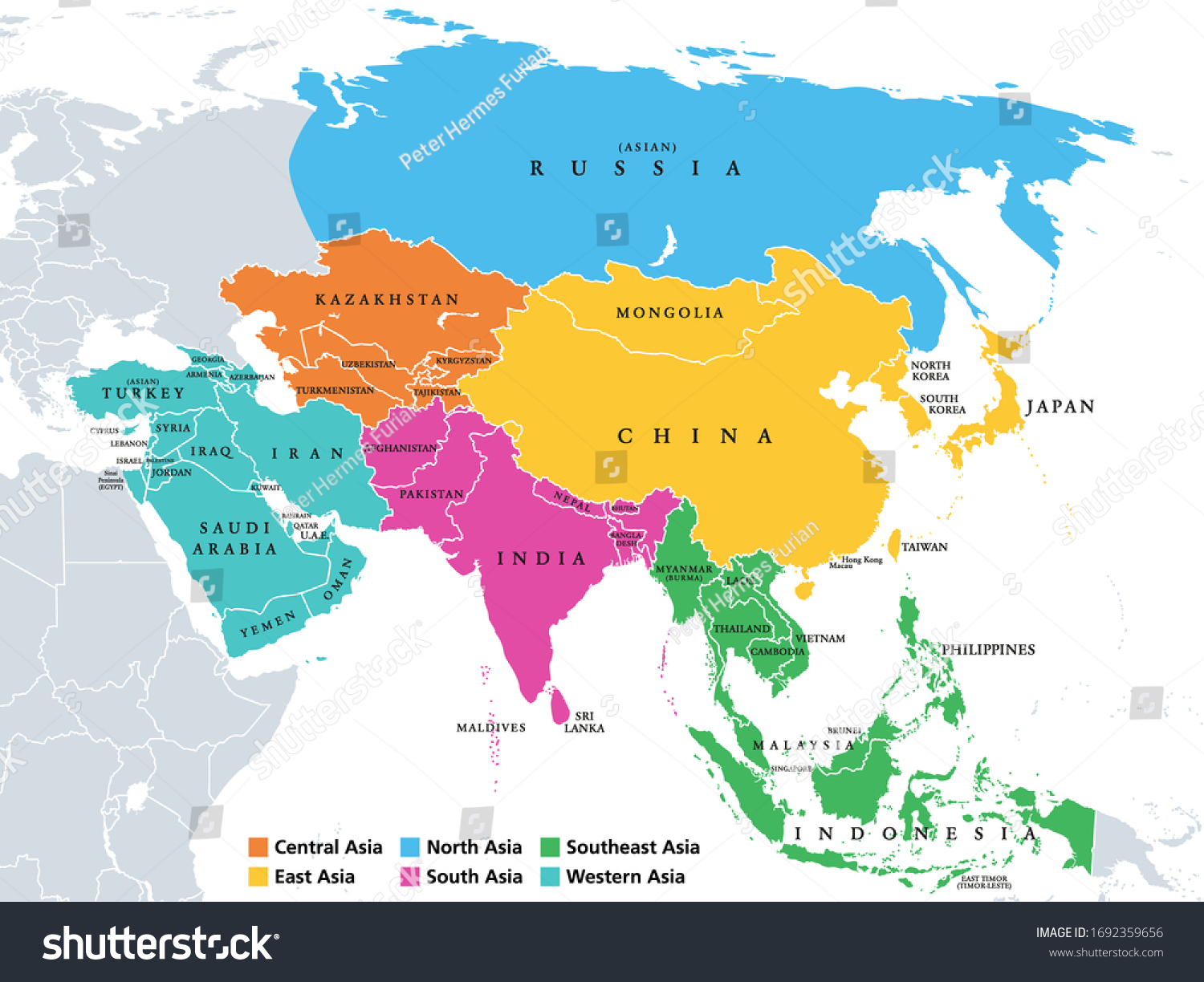
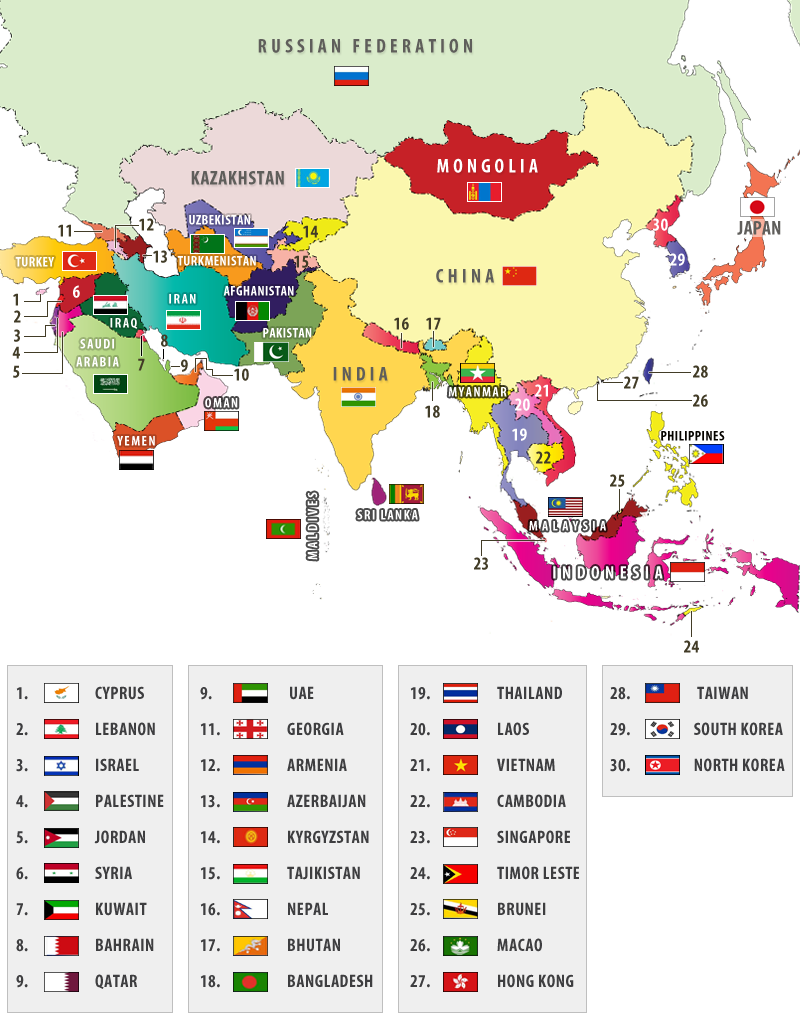
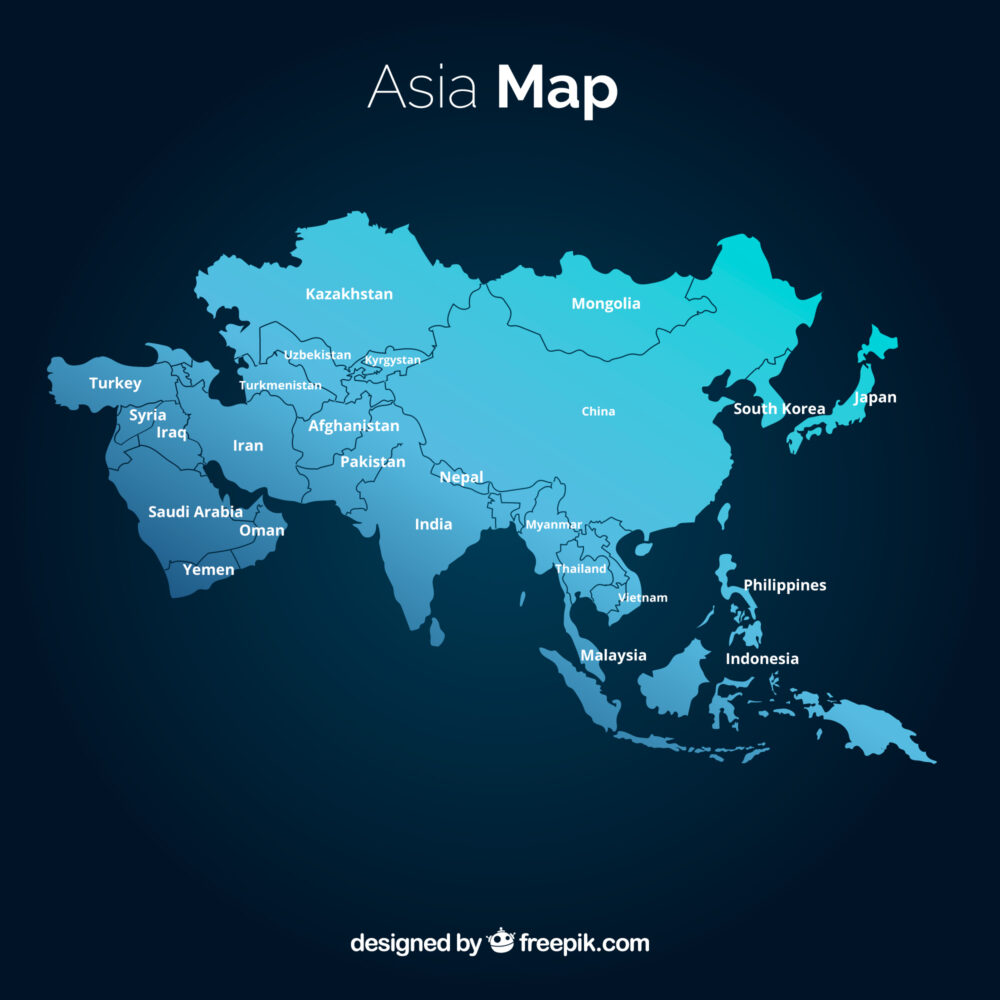
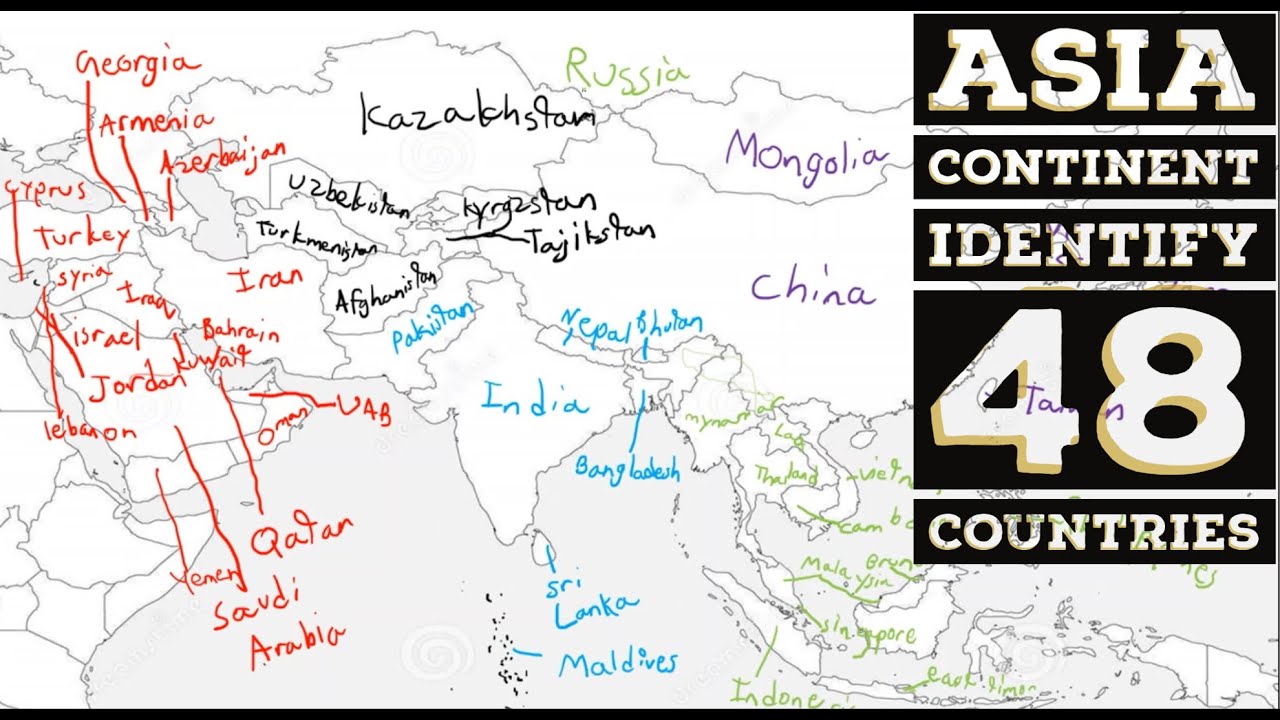
Political Landscape: 48 Countries and Their Diverse Identities
The political landscape of Asia is equally diverse, with 48 sovereign states exhibiting a range of political systems, economic structures, and cultural traditions. These countries are:
Eastern Asia:
- China: The world’s most populous country, China is a major economic and military power.
- Japan: A technologically advanced nation known for its economic prowess and cultural influence.
- South Korea: A rapidly developing nation with a thriving economy and a strong cultural presence.
- North Korea: A communist state with a closed economy and a history of political isolation.
- Mongolia: A landlocked country with a rich nomadic heritage and a growing economy.
- Taiwan: A self-governing island with a vibrant democracy and a strong economy.
Southeast Asia:
- Brunei: A small, oil-rich sultanate with a rich cultural heritage.
- Cambodia: A country recovering from decades of conflict, with a rich history and a growing tourism industry.
- East Timor: A young nation with a strong sense of national identity and a burgeoning economy.
- Indonesia: The world’s largest archipelago, with a diverse population and a rapidly growing economy.
- Laos: A landlocked country with a rich cultural heritage and a growing tourism industry.
- Malaysia: A multiethnic nation with a diverse economy and a vibrant cultural scene.
- Myanmar (Burma): A country undergoing political and economic reforms, with a rich history and a diverse population.
- Philippines: An archipelago nation with a vibrant culture and a growing economy.
- Singapore: A city-state known for its economic dynamism and its multicultural society.
- Thailand: A popular tourist destination with a rich history and a vibrant culture.
- Vietnam: A country with a long history and a rapidly growing economy.
Southern Asia:
- Afghanistan: A landlocked country with a long history of conflict and a complex political landscape.
- Bangladesh: A densely populated country with a rapidly growing economy and a rich cultural heritage.
- Bhutan: A small, mountainous country known for its stunning scenery and its unique cultural traditions.
- India: The world’s second most populous country, with a diverse population, a rapidly growing economy, and a rich cultural heritage.
- Maldives: A tropical archipelago nation known for its beautiful beaches and its luxury resorts.
- Nepal: A mountainous country with a rich cultural heritage and a growing tourism industry.
- Pakistan: A country with a diverse population and a complex political landscape.
- Sri Lanka: An island nation with a rich history and a vibrant culture.
Central Asia:
- Kazakhstan: A large, landlocked country with a diverse population and a growing economy.
- Kyrgyzstan: A mountainous country with a rich cultural heritage and a growing tourism industry.
- Tajikistan: A mountainous country with a rich cultural heritage and a growing economy.
- Turkmenistan: A country with vast oil and gas reserves and a unique cultural heritage.
- Uzbekistan: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
Western Asia:
- Armenia: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- Azerbaijan: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- Bahrain: A small island nation with a rich cultural heritage and a growing economy.
- Cyprus: An island nation with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- Georgia: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- Iran: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a complex political landscape.
- Iraq: A country with a rich history and a complex political landscape, with a growing economy.
- Israel: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a complex political landscape.
- Jordan: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- Kuwait: A small, oil-rich country with a growing economy.
- Lebanon: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a complex political landscape.
- Oman: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- Qatar: A small, oil-rich country with a growing economy.
- Saudi Arabia: The world’s largest oil exporter, with a rich cultural heritage and a complex political landscape.
- Syria: A country with a rich history and a complex political landscape, with a growing economy.
- Turkey: A country with a rich history and a vibrant culture, with a growing economy.
- United Arab Emirates: A federation of seven emirates, with a growing economy and a vibrant cultural scene.
- Yemen: A country with a rich history and a complex political landscape, with a growing economy.
Regional Cooperation and Challenges
The countries of Asia are increasingly engaged in regional cooperation, particularly in areas such as trade, investment, and security. Regional organizations such as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) have played a significant role in fostering regional cooperation.
However, Asia also faces a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. These challenges require regional cooperation and international collaboration to address.
Economic Dynamics
Asia is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, including China, India, and South Korea. The region’s economic growth is driven by a number of factors, including a large and growing population, a young and dynamic workforce, and a rapidly expanding middle class.
However, Asia’s economic growth is not without its challenges. The region faces a number of economic disparities, with some countries experiencing rapid growth while others struggle to develop. Furthermore, Asia’s economic growth is often accompanied by environmental degradation and social inequality.
Cultural Tapestry
Asia is a continent of immense cultural diversity, with a rich history of art, literature, music, and religion. The region is home to a number of major world religions, including Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, and Christianity. Asia’s cultural heritage is reflected in its diverse cuisine, its traditional arts and crafts, and its vibrant festivals.
Challenges and Opportunities
Asia is a region of immense opportunity, but it also faces a number of challenges. These include:
- Poverty and Inequality: Despite its economic growth, Asia remains home to a large number of people living in poverty. The region also faces significant inequality, with a small elite controlling a disproportionate share of wealth.
- Environmental Degradation: Asia’s rapid economic growth has come at a cost to the environment. The region faces a number of environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
- Political Instability: Asia is home to a number of countries with complex political landscapes. Political instability can lead to conflict, violence, and economic stagnation.
- Terrorism: Terrorism is a growing threat in Asia, with groups such as al-Qaeda and ISIS operating in the region. Terrorism can destabilize countries, undermine economic growth, and threaten regional security.
Conclusion:
Asia is a continent of immense diversity, with 48 countries each contributing to its unique identity. From the towering Himalayas to the bustling cities of Tokyo and Shanghai, Asia is a region of breathtaking beauty, rich history, and vibrant culture. While the continent faces a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation, it also presents immense opportunities for economic growth, technological innovation, and regional cooperation. Understanding the complexities of Asia is crucial for navigating the 21st century, a century where Asia will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the global landscape.
FAQs
Q: Why is it important to understand the map of Asia with 48 countries?
A: Understanding the map of Asia with 48 countries is essential for comprehending the geopolitical dynamics, cultural diversity, and economic potential of the continent. It provides a framework for analyzing regional relationships, identifying areas of conflict and cooperation, and understanding the impact of global events on different parts of Asia.
Q: What are the key challenges facing Asia in the 21st century?
A: Asia faces significant challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, political instability, and terrorism. These challenges require regional cooperation and international collaboration to address.
Q: What are the key opportunities for Asia in the 21st century?
A: Asia presents immense opportunities for economic growth, technological innovation, and regional cooperation. The continent’s large and growing population, young workforce, and rapidly expanding middle class offer significant potential for development.
Q: What are some of the key regional organizations in Asia?
A: Key regional organizations in Asia include ASEAN, SAARC, and SCO. These organizations play a significant role in fostering regional cooperation in areas such as trade, investment, and security.
Tips
- Use a high-quality map: A detailed map with clear borders and country names will be invaluable for understanding the geography of Asia.
- Focus on regional divisions: Pay attention to the different regions within Asia, such as Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Central Asia.
- Explore cultural diversity: Research the different cultures, languages, and religions of Asia.
- Consider economic factors: Examine the economic strengths and weaknesses of different Asian countries.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up-to-date on current events in Asia, as they can significantly impact the region’s political and economic landscape.
Conclusion
The map of Asia with 48 countries is more than just a geographical representation; it is a visual testament to the continent’s diversity, complexity, and significance. It serves as a tool for understanding the intricacies of regional relationships, the challenges faced by Asian nations, and the opportunities that lie ahead. As Asia continues to play an increasingly important role in the global landscape, understanding this map becomes crucial for navigating the complex dynamics of this vast and dynamic continent.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Asia: 48 Countries and a Continent of Diversity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!