A Comprehensive Guide to Asia: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of a Continent
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Asia: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of a Continent
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Asia: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of a Continent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Asia: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of a Continent

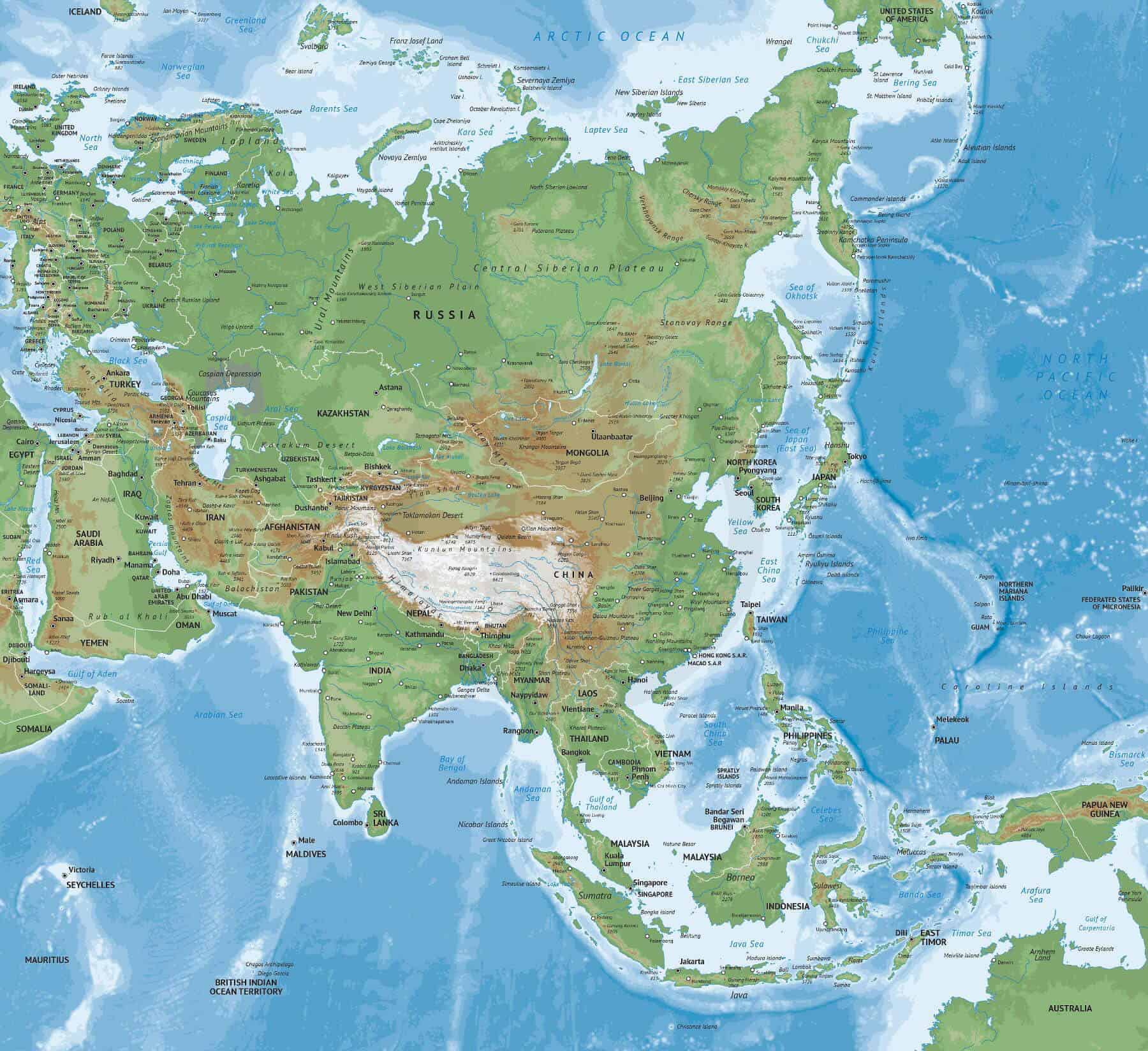
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories. Its sprawling expanse, encompassing 49 countries and numerous territories, presents a captivating mosaic of civilizations, each with its unique story to tell. Understanding the geography and political landscape of Asia is crucial for comprehending its global influence and navigating the complexities of its geopolitical landscape.
Navigating the Asian Landscape: A Geographic Overview
Asia’s vastness is both its strength and its challenge. Its geographical boundaries extend from the eastern edge of the Ural Mountains in Europe to the Bering Strait in the north, encompassing a vast stretch of landmass stretching south to the Indian Ocean and the Indonesian archipelago. The continent is divided into several distinct regions, each with its own geographical features and cultural characteristics:
1. East Asia: This region encompasses China, Japan, South Korea, North Korea, Mongolia, and Taiwan. East Asia is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with several major rivers like the Yangtze and Yellow rivers providing fertile land for agriculture. It is also home to some of the world’s most densely populated cities, including Tokyo, Shanghai, and Seoul.
2. Southeast Asia: This region includes Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos, Brunei, the Philippines, and Timor-Leste. Southeast Asia is characterized by its tropical climate, diverse ecosystems, and numerous islands. It is a region of significant cultural and religious diversity, with Buddhism, Islam, and Christianity all playing prominent roles.
3. South Asia: This region comprises India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, Maldives, and Afghanistan. South Asia is home to the Indus River Valley, the Ganges River, and the Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range. It is also a region of immense cultural and religious diversity, with Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, and Sikhism all having significant followings.
4. Central Asia: This region includes Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Afghanistan. Central Asia is characterized by its arid climate, vast steppes, and mountain ranges. It is historically known for its role in the Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting East Asia with Europe.
5. West Asia: This region, also known as the Middle East, includes Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine, Kuwait, Bahrain, Oman, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. West Asia is characterized by its deserts, oil reserves, and its strategic location between Africa, Europe, and Asia. It is a region of significant religious and political importance, home to Islam’s holiest sites.
The Political Landscape: A Mosaic of Nations
Asia’s political landscape is as diverse as its geography. The continent is home to a wide range of political systems, from democracies to monarchies to communist states. Several key factors have shaped the political landscape of Asia, including:
1. Colonial History: The colonial legacies of European powers have had a profound impact on Asia’s political landscape. Countries like India, Pakistan, and Indonesia gained independence in the 20th century, but the legacies of colonialism continue to shape their political systems and economic structures.
2. Cold War Rivalries: The Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union also left its mark on Asia. The Korean War and the Vietnam War were major conflicts that resulted in the division of Korea and the establishment of communist regimes in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia.
3. Economic Growth and Development: The rapid economic growth experienced by many Asian countries in recent decades has also had a significant impact on their political systems. The rise of China and India has created new power dynamics in the region, leading to increased competition and cooperation among Asian nations.
4. Regional Conflicts and Tensions: Asia is also home to numerous regional conflicts and tensions, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the territorial disputes in the South China Sea, and the ongoing conflict in Afghanistan. These conflicts pose significant challenges to regional stability and cooperation.
The Importance of Asia in the Global Landscape
Asia’s significance in the global landscape cannot be overstated. The continent is home to a significant portion of the world’s population, resources, and economic activity. Its growing economic power, coupled with its strategic location, makes it a key player in global affairs.
1. Economic Powerhouse: Asia is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, including China, India, South Korea, and Singapore. The region’s economic growth has fueled global trade and investment, contributing significantly to global economic development.
2. Global Trade and Investment: Asia is a major player in global trade and investment. It is a major producer of goods and services, and it is also a significant destination for foreign investment. The region’s economic growth has been driven by its manufacturing sector, its technological advancements, and its growing consumer market.
3. Strategic Location: Asia’s strategic location between Europe, Africa, and the Americas makes it a key player in global geopolitics. The region’s control over vital sea lanes and its vast resources make it a focal point for international relations.
4. Cultural and Religious Diversity: Asia is home to a rich tapestry of cultures and religions. Its diverse societies have contributed significantly to global art, literature, music, and philosophy. The region’s cultural and religious diversity also poses challenges to regional stability and cooperation.
Navigating the Complexities of Asia: FAQs
1. What are the major languages spoken in Asia?
Asia is home to a vast array of languages, with hundreds of distinct languages spoken across the continent. Some of the most widely spoken languages include Mandarin Chinese, Hindi, Bengali, Urdu, Japanese, English, Russian, Arabic, and Korean.
2. What are the major religions practiced in Asia?
Asia is home to a wide range of religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, Christianity, Sikhism, Confucianism, Taoism, and Judaism. The dominant religions vary from region to region, with Hinduism prevalent in South Asia, Islam in West Asia and parts of Southeast Asia, Buddhism in East and Southeast Asia, and Christianity in the Philippines and parts of Southeast Asia.
3. What are some of the major challenges facing Asia?
Asia faces numerous challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, political instability, and regional conflicts. These challenges require coordinated efforts from governments, international organizations, and civil society to address.
4. What are some of the opportunities for Asia in the future?
Asia has significant potential for future growth and development. Its growing economies, its vast resources, and its young population present opportunities for innovation, economic progress, and regional cooperation.
Tips for Understanding Asia
1. Engage with Different Cultures: Travel, read, and learn about the diverse cultures and traditions of Asia. Attend cultural events, interact with people from different backgrounds, and explore the region’s rich history.
2. Embrace the Diversity: Recognize and appreciate the diversity of Asia’s languages, religions, and customs. Avoid making generalizations and be open to learning about different perspectives.
3. Stay Informed about Current Events: Follow news and developments in Asia to gain a better understanding of the region’s political, economic, and social landscape.
4. Support Sustainable Development: Advocate for policies and practices that promote sustainable development in Asia, addressing environmental concerns, promoting economic growth, and reducing poverty.
Conclusion
Asia is a continent of immense complexity and dynamism. Its vast geography, diverse cultures, and evolving political landscape present both opportunities and challenges. Understanding Asia’s history, geography, and political landscape is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st century. By embracing its diversity, promoting regional cooperation, and addressing its challenges, Asia can continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the global future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Asia: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of a Continent. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!